We all know how vital each component of musical equipment is in producing excellent sound quality and an engaging listening experience. When it comes to speaker wires, coaxial speaker cables are outstanding in transmitting high-quality audio signals between audio components and speakers. These cables decrease signal loss and interference due to their unique structure and design, resulting in improved sound clarity and fidelity.
In this article, we will go through the features, benefits, and things to think about while utilizing coaxial speaker cables in your audio system.
Outline
Toggle- What is a Coaxial Speaker Cable?
- What Makes a Coaxial Cable?
- How Does it Differ From Digital Coaxial Cables?
- Types of Coaxial Speaker Cable
- Sizes of Coaxial Speaker Cable
- Impedance of Coaxial Speaker Cables
- Types of Connectors for Coaxial Cables
- Comparison: Coaxial Vs Optical Vs HDMI cables
- How to Choose the Right Coaxial Speaker Cable?
- Coaxial Speaker Cable – FAQs
What is a Coaxial Speaker Cable?
Coaxial cable is widely utilized to receive visual and audio signals through composite and component connectors in cable television, audio systems, radio, video equipment, and game consoles.
A coaxial speaker cable is a shielded and insulated electric conducting wire that contains an inner metal conductor and woven copper covering for delivering high-frequency ad high-speed data over long distances.
These days coaxial cables are wide-reaching:
- Home stereo systems (including speaker connections).
- Audio recording with a microphone.
- Connect electric musical instruments to amplifiers.
What Makes a Coaxial Cable?
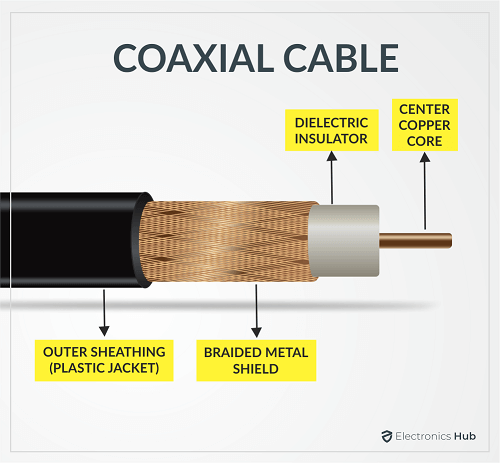
While there are multiple kinds of coaxial cables with distinct designs for numerous uses, all coaxial cables contain four essential components. These components are listed in order of appearance from the outside to the center:
- Core conductor
- Dielectric insulator
- Metal shield
- Plastic jacket
| Components of a Coaxial Cable |
| 1. The Central Core Conductor
This is the part that does the work: it transmits the signal and serves as an electrical grounding for the cable. These are frequently made of copper, although they can also be built of steel with a copper wire covering. A dielectric insulator is wrapped around the core copper conductor. |
| 2. The Inner Dielectric Insulator
The insulator exists to separate the metallic shield from the core wire. Depending on the kind of coaxial cable, the type of insulators merged into the core wire may vary from foam plastic, solid plastic (or) air spacers. It also has a PVC-coated sheath, making the insulator’s outer layer easy to stretch. |
| 3. The Woven Copper Metallic Shield
You can often find a coaxial cable with two shields, which is braided copper wire with aluminum foil. This component protects the signal being transmitted against radio wave interference. |
| 4. The Outer Plastic Jacket
The cable’s external plastic jacket, which is typically made of Polyvinyl Chloride, protects the internal components of the cable that manage signal transmission and interference protection. |
How Does it Differ From Digital Coaxial Cables?
Coax cable and digital coax cable may be puzzling for people who are unfamiliar with different speaker wires. So, let us look into how a digital coax cable varies from a standard coax cable.
- Even digital coaxial audio cables are designed to transmit crystal-clear audio signals from an amplifier to a speaker like a standard coaxial cable.
- Moreover, they are engineered in a similar way to serve the same purpose. The digital coax cables include a center wire made of insulation material, a plastic casing, and a metallic shield.
- Coaxial digital audio cables can be connected to cable boxes, cable TV modems, runners, satellites, radios, TV antennas, home speakers, high-end speakers, Blu-ray players, and many more because of their wide audio and video applications.
- Audiophiles preferably opt for digital audio coaxial cables for their ability to handle a wide variety of electrical frequencies. Although digital coaxial audio cables can carry electrical frequencies over a wide range of audio frequencies, they cannot handle higher-quality, multi-channel audio formats like standard coaxial wires.
Types of Coaxial Speaker Cable
Coaxial speaker wires are broadly classified into different types based on RG standards, features, characteristics, and construction to meet diverse audio system requirements.
| Different Types of Coaxial Cables |
1. Hardline Coaxial Cable
|
2. Subwoofer Coaxial Cable
|
3. Flexible Coaxial Cables
|
4. Micro Coaxial Cable
|
5. Rigid Coaxial Cables
|
6. Semi-Rigid Coaxial Cables
|
7. Formable Coaxial Cable
|
8. Twin Coaxial Cable
|
9. Triaxial Cable
|
10. Radiating Coaxial Cable
|
11. Miniature Coaxial Cables
|
12. High-Temperature Coaxial Cables
|
13. High-Frequency Coaxial Cables
|
14. Water-Cooled Coaxial Cable
|
15. Coaxial Ribbon Cable
|
Sizes of Coaxial Speaker Cable
Coaxial cables are manufactured in various sizes to serve various purposes. Here is a list of some commonly used cable sizes.
1. RG-6 Coaxial Cable
- RG-6 coaxial cables have a core diameter of 1.024 mm and an outer diameter ranging from 6.86 mm to 7.57 mm with an impedance of 75Ω for transmitting high-quality videos and data without any signal loss.
- F-type connectors are often used to terminate RG-6 coaxial wire, providing a secure and durable connection. These coaxial cables are used in cable television, satellite television, broadband internet, and video surveillance systems.
- RG-6 coaxial cables are perfect for lengthy cable runs as it supports efficient signal transmission over long distances.
2. RG-7 Coaxial Cable
- RG-7 coaxial cables have a core diameter of 1.3 mm and an outer diameter of 8.13 mm with an impedance of 75Ω for high-quality video and data transmission with signal integrity.
- F-type connectors are used to terminate RG-7 coaxial wire, providing a secure and durable connection. Even, these coaxial cables are used in cable television, satellite television, and modems.
3. RG-8 Coaxial Cable
- RG-8 coaxial cables have a core diameter ranging from 1.47 mm to 2.17 mm and an outer diameter ranging from 6.1 mm to 10.3 mm with an impedance of 50Ω for high-frequency digital transmissions.
- RG-8 coaxial cables are commonly used for radio transmissions since it is an ideal match for various transmitter antennas and radio transmitters.
4. RG-11 Coaxial Cable
- RG-11 coaxial cables have a core diameter of 1.63 mm and an outer diameter of 10.5 mm with an impedance of 75Ω for high-quality data transmission.
- These heavy-duty coaxial cables can handle and support a wide variety of frequencies up to 3 GHz (or) more for reliable digital transmissions over long distances.
- They are used in signal transmission applications like satellite signals, large-scale cable TV distribution networks, and broadband internet traffic that need low signal loss and good performance.
5. RG-56 Coaxial Cable
- RG-56 coaxial cables have a core diameter of 1.49 mm and an outer diameter of 7.82 mm with an impedance of 48Ω for high-voltage signal transmission.
- They are commonly designed to handle voltages up to 8000 v and are used in high-voltage applications.
6. RG-58 Coaxial Cable
- RG-58 coaxial cables have a core diameter of 0.81 mm and an outer diameter of 5 mm with an impedance of 50Ω for effective communications.
- They are ideal for radio communications, amateur radio, and nuclear electronic instruments.
7. RG-59 Coaxial Cable
- RG-59 coaxial cables have a core diameter of 0.64 mm and an outer diameter of 6.1 mm with an impedance of 75Ω for low-frequency data transmission without signal loss.
- They are mostly used for lower-frequency video and audio applications, such as CCTV systems, video surveillance installations, and older composite video connections.
8. RG-60 Coaxial Cable
- RG-60 coaxial cables have a core diameter of 1.024 mm and an outer diameter of 10.8 mm with an impedance of 50Ω for high-voltage signal transmission.
- They are commonly designed to handle high-speed applications such as HD cable TV, High-speed cable internet, etc.
Have a glance at the Radio Guide (RG) standard for a quick overview.
| RG cable | Impedance | Core diameter | Outer diameter | Applications |
| RG-6 | 75Ω | 1.024 mm | 6.86 mm – 7.57 mm | Cable TV, satellite TV, and modem |
| RG-7 | 75Ω | 1.3 mm | 8.13 mm | Cable TV, satellite TV, and modem |
| RG-8 | 50Ω | 1.47 mm – 2.17 mm | 6.1 mm – 10.3 mm | Amateur radio |
| RG-11 | 75Ω | 1.63 mm | 10.5 mm | High-frequency applications like cable TV and satellite TV |
| RG-56 | 48Ω | 1.49 mm | 7.82 mm | All high-voltage applications |
| RG-58 | 50Ω | 0.81 mm | 5 mm | Radio communications, amateur radio, and nuclear electronic instruments |
| RG-59 | 75Ω | 0.64 mm | 6.1 mm | CCTV, RF Video Transmission with HD and Ultra High-Quality |
| RG-60 | 50Ω | 1.024 mm | 10.8 mm | HD cable television and high-speed cable internet |
Impedance of Coaxial Speaker Cables
The impedance is an important factor that distinguishes coaxial cables. This feature represents the degrees of power transmission and standing waves and also impacts the cable’s compatibility with the speaker system. The most common impedance values are as follows.
| 50Ω |
|
| 75Ω |
|
| 93Ω & 52Ω |
|
Types of Connectors for Coaxial Cables
There are several types of connectors used for coaxial cables in conjunction with their RG classification type. Listed below are some of the most popularly used connectors.
| Kinds of Connectors for Coaxial Cables |
BNC Connector
|
N-type Connectors
|
SMA Connectors
|
F-type Connectors
|
RCA Connectors
|
MCX Connectors
|
Comparison: Coaxial Vs Optical Vs HDMI cables
- The coaxial connections have a higher bandwidth range than an optical digital connection since they provide greater capacity for various services such as voice, multimedia, video, and even data.
- The optical connections reduce noise traveling from the source device to the circuit. They can be directly linked to the DAC of AV receivers and the optical fibers are used in optical communication cables instead of copper wires.
- Although coaxial cables may transmit more data than an optical digital link but both of these cables are incapable of supporting lossless audio formats. Plus installation of coaxial wires is pretty simple than optical connections.
- When compared to coaxial and digital optical lines, an HDMI connection provides unrivaled bandwidth. These connections can support all sound formats including Dolby Digital, Dolby TrueHD, Dolby Atmos, and DTS Master Audio.
- Moreover, HDMI cables work well with the video formats such as 4K Ultra, HD resolutions, and multiple HDR combinations. This connection is commonly found in source devices such as an AV receiver, soundbar, and television.
Benefits and Limitations of Coaxial Speaker Cable
Coaxial cables are an excellent option to carry the signal from your receiver (or) amplifier to your speakers as they carry high-frequency signals with minimal interference. Here is the list of advantages and disadvantages of coax cables.
Advantages of Coaxial Cables
- High-quality audio signals are transmitted at a higher-speeds.
- These cables are simple to set up and are extremely long-lasting.
- Designed with excellent shielding against interference (or) noise from other transmissions.
- Delivers reliable performance and better sound quality over shorter distances.
- They are widely used in professional settings because of their excellent endurance and ability to create superior digital audio.
- They are highly affordable without compromising video and audio transmission quality.
- Coaxial cables are adaptable and may be utilized in a variety of sectors and contexts, including TV and radio transmission, home entertainment systems, security systems, and data networking.
Disadvantages of Coaxial Cables
- Signal loss is an issue with lengthy wires.
- Coax cables are more difficult to conceal as they are larger, heavier, and less flexible.
- Highly sensitive to electromagnetic interference.
- Compatible with only some audio devices.
- It is more difficult to terminate (or) end precisely.
- Coaxial setups do not support popular sound systems such as DTS-HD Master Audio.
How to Choose the Right Coaxial Speaker Cable?
Here are some of the important factors that must be considered while selecting a coaxial speaker cable.
1. Cable Gauge
Usually, the gauge of a cable refers to the wire’s thickness (or) diameter. Thicker cables offer lower resistance and are capable of supporting higher power levels.
Generally cables with smaller gauges such as 12 (or) 14 are suggested for higher-powered speaker systems whereas the cables with larger gauges such as 16 (or) 18 can be used for lower-powered systems.
2. Cable Material
Choose cables made of high-quality materials for excellent signal transmission and durability. However, copper is widely used for speaker cables because of its excellent conductivity characteristics. Moreover, go for cables with appropriate insulation and shielding to prevent signal interference and retain signal integrity.
3. Cable Length
First, measure the distance and select the length of wire needed for your speaker system. Check that the wire is not excessively long or too short. Always use a long enough wire to connect the audio source to the speakers. And avoid leaving excessive cable length since it may cause signal loss and reduce audio quality.
4. Connector Type
Choose the right connection type for your speakers and audio equipment. Make sure that the connectors you select are made of high-quality materials to provide a safe and reliable connection, eliminating signal loss, and ease of installation.
5. Budget
Set your budget before purchasing the coax cables. Choose the cable that is compatible with your audio system and accommodates the required features. However, there are multiple cables with abundant features that come in an affordable range.
6. Reviews
We always recommend you read the feedback shared by other users from various online platforms before purchasing the cables. Genuinely, these reviews will help you understand the performance of the cables and get the right one according to your needs.
Conclusion
Winding up, coaxial cables are an everyday component of audiophile equipment, with applications ranging from cable boxes to audio and video signal transmission and even speaker connections. They are a form of electrical cable that can transfer radiofrequency (RF) signals. And that’s all about coaxial speaker cables. We hope this article has included all the important aspects including what they are, classification, benefits, limitations, and the factors that must be considered while choosing the right coax cable that suits your requirements.
These days, many people are gravitating to coax cables because of their cost, high-bandwidth transmission, and durability. We hope even you will use it as a speaker wire because of its low induction and thick conductor. Please let us know…
Coaxial Speaker Cable – FAQs
Ans: Yes, a coaxial cable works well for audio transmission. Apart from standard speakers and subwoofers, coax wires can also be used as microphone cables due to their ability to produce low frequencies to high noise ratios.
Ans: Coaxial cables can be utilized as subwoofer cables over long distances greater than 40 feet because of their improved shielding and lower cost.
Ans: RG-6 coaxial wire is one of the most prevalent and commonly used varieties of coaxial cables. It is often used for cable television installations, satellite television installations, and high-speed internet connections.
Ans: Of course, you can connect multiple coaxial cables together using coaxial connectors (or) couplers for extending the cable length for longer runs.
Ans: Yes, coaxial cables can be used for outdoor installations. In fact, they are specifically designed with weatherproofing and UV-resistant jackets to withstand exposure to the elements and provide reliable signal transmission in outdoor environments.
Ans: RG-6 and RG-11 coaxial cables are widely employed for internet connections to deliver the bandwidth and signal integrity required for high-speed data transmission in cable internet and broadband applications.
Ans: Yes, coaxial-to-speaker wire adapters are available. They have a coaxial input on one end and speaker wire connectors on the other end. These adapters are used to convert a coaxial connection to a speaker wire connection.

