Tack weld is a method of temporary welding that serves as the base guideline for the final welding. In tack welding, tiny beads of the filler material are placed throughout the joints of the workpieces. The number and density of the dots depend on the material of the workpiece and its depth. The beads are called tack welds.
Even though it may not seem significant at first glance, it is essential to welding professionals. The tack welds work as a guideline for welding and the final layout.
Even though tack welds are temporary, these are of high quality and the same filling material of the original welding method is also used for tacks.
Outline
ToggleWhat Is The Use Of a Tack Weld?
The primary purpose of tack welding is to keep the workpieces joined together so that the final welding can be executed successfully.
On top of that, the tack welds keep the edges of the workpieces together and maintain the gap.
Tack weld is also used in some welding methods to prevent wedge distortion.
It works as a rough project layout so that errors can be easily fixed. That means if the edges are tack welded the wrong way, the welder can remove the racks and redo the alignment in the right way.
Tack welds maintain the welding position and orientation to prevent issues like overturning or wrongly joined work pieces.
Tack welds improve the functions of fixtures used in welding. In some cases, tanks are used instead of fixtures also.
Advantages Of Tack Welding
- It offers an outlay to create the final welding to join two or more work pieces.
- Tacks can be undone and disabled if these are placed wrong
- Tacks help to strengthen the joint and maintain the joint gap properly
- Tacks are used to smoothen and fill out if there is a gap even after the final welding
- Tacks help to prevent joint distortion during welding
- You can tack weld almost every type of material used for welding
Disadvantages Of Tack Welding
- If the tacks are not placed with proper planning, it can decrease the efficiency of the final welding.
- Tacks may trap some slag inside them if not cleaned carefully
- The post-welding cleaning is complicated and time-consuming
- You need to choose the proper tack welding technique depending on the metal. Otherwise, it may not help at all.
- Sometimes, it becomes challenging to remove tacks, especially in steel and thinner work pieces.
How Does It Work?
In the case of tack welding, the same method that is chosen for the final welding is used.
But, instead of the final welding machine, a smaller machine is used to apply the tacks of metal beads. In other words, it is usually done on a small scale.
In this case, a smaller electrode and a smaller torch or stud gun are used. It allows the welder to place small metal dots throughout the edge without melting the edges too much.
The filler material is heated, and the surface of the base material is heated to a lesser depth. Then the tacks are placed on the edges on ¼ th to ½ th inch gap.
In the case of stick welding or flux core welding, the tacks are used with the same machine. But, for thinner or more expensive materials, the welder may need to pre-plan the tack alignment. For example, the tacks must be placed after proper planning in TIG or Tungsten Inert Gas welding.
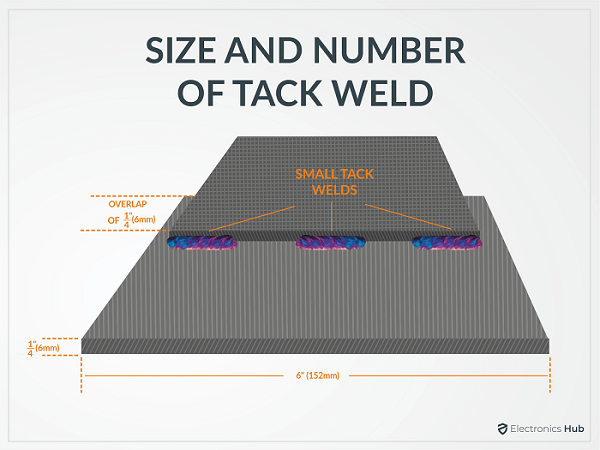
1. The Size And Number Of Tack Welds
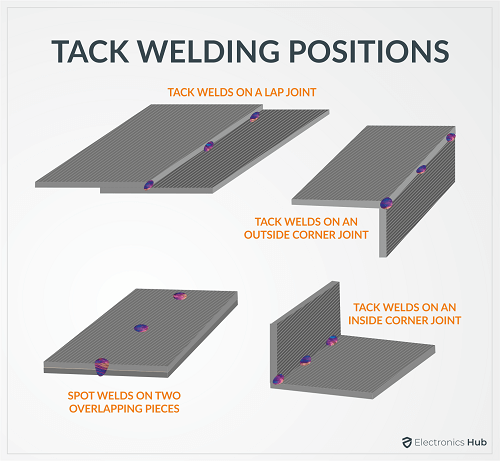
2. Tack Weld Position
3. Stick Welding Tacks
The most complicated tack welding procedure is the stick welding tacks, as, with time, the arc gets consumed, and the constant smoke often poses a visibility challenge. On top of that, the consumable electrode should be adequately controlled, which can become defective.
Some welding electrodes are difficult to handle, especially after the tack welding process starts. If the filler material burs more than the flux coating, there can be challenges. In such cases, the arc may not start as the rod’s tip is way inside, and it is difficult to scratch the flux. In such cases, restarting the arc becomes more difficult.
Hence, the welding expert often uses a metal file to remove the excess flux coating to restart the process. The E7018 core often leads to this type of issue. On the contrary, the E6010 and E6011 cores are tremendous and offer smooth restart for tack welding.
On top of that, slag also imposes more tack challenges as the sagas weaken the tack. Hence, welders often do not use the E6013 core.
4. TIG Welding Tacks
TIG welding is often used for tacks as it is more precise and can be easily used on a small scale. Since the tungsten core is non-consumable and has high-temperature resistance, it does not create smoke and keeps the feasibility intact.
On top of that, you can also apply tacks without using filler materials. Sharper tungsten cores are better as they narrow the arc some and focus the heat on a smaller area, increasing precision. In the case of thicker work pieces, lanthanide tungsten electrodes are ideal.
Experts recommend filler rods of the same thickness as the base work piece to prevent unnecessary burning.
5. MIG/FCAW Tack Welds
MIG or FCAW tack welds are also significant, and the touch allows you to precisely melt the joint and create properly sized tacks with the wire feeder. In this case, smaller torches are used.
If you want to best results, follow these hacks–
- Smaller wires are ideal because these wires deposit only a tiny drop of metal on the joint, making tacks precise.
- Always increase voltage output as it amplifies the arc’s push effect, creating flatter tacks.
- Keeps the wire feeding speed low to prevent burning on the wire and base material
- Always make sure to chip the wire before applying each tack.
How To Tack Weld Metal
There are multiple strategies for performing tack welding. But here are the two most used methods-
- Start with the end and then bisect-In this method; the tracks are placed on the ends of the workpiece Then move inside and place tack at the middle of the joint length. Then go back and forth. It is better to mark the places where you want to place tracks if the material is sensitive and requires high precision.
- Move to the ends from the middle- First, you can make marks to find the middle point of the joint line. Now, move towards the ends alternating on both sides on the desired places. Place a tack at this exact point.
Types Of Tack Welds
1. Standard Tack Weld
Standard track welding refers to conventional tack welding, where the tacos offer support for the final welding. In this case, the tracks significantly add extra support and prevent breaking from the joint.
2. Bridge Tack Weld
Bridge tack welding is used when the welded joint needs a root opening for inserting pipes or other items in the gap. The primary purpose of this method is to keep the gaps intact while keeping the work pieces joined together. It is mainly used before flux-coated welding, TIG and MIG welding.
In this case, small tacks are applied to the work pieces so each side gets enough time to cool before applying the next tack. Interestingly, the bridge tacks usually do not go deep to the root of the joint and are usually applied at a shallow depth. It is because these tacks are removed after making the first root pass.
3. Hot Tack Weld
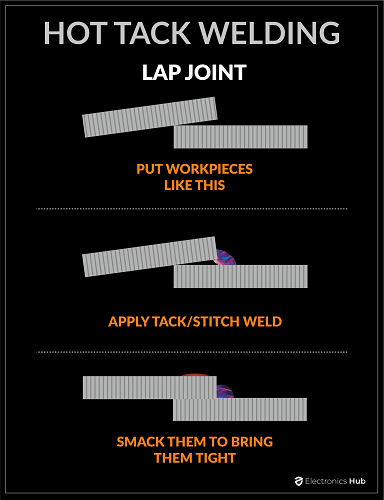
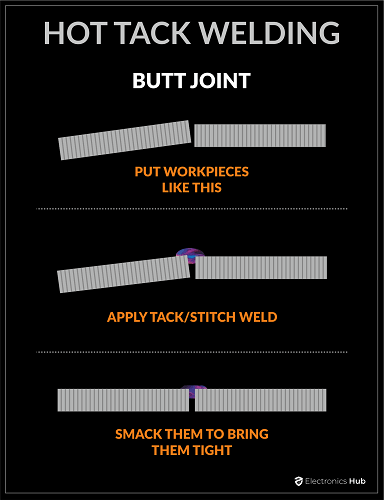
4. Ultrasonic Tack
The welder creates small tacks on the joints of the edges with small electric or gas welding machines. The machine pushes through the workpiece joints at ultrasonic speed to push the molten filler materials into those tiny holes to create tacks.
Materials That Can Be Tack Welded
For tack welding, a welder can use filters, including steel. Alloy steel, Carbonated steel, Stainless steel, Cast iron, brass and copper or even magnesium or titanium alloy. In most cases, the tracks are of the same material from which the work pieces are made.
Tack welding can be used on stainless steel, alloy steel, copper, brass, cast iron etc. But, one must always choose the correct tack welding technique to get the desired result.
Conclusion:
Tack welds are used as a guideline and preparation for the final welding. One of the best advantages of a tack weld is that it can be placed easily. But, while placing tacks, one must place those in the correct measurement to ensure the final result is precise and serves its purpose.
If done correctly, tack welds off a lot of support to the joint and keeps the welding smoother without any distortion or error in the final welding.

