Arranging or sorting your sockets based on the size may sound easy. But it is not. Especially when there are two measurement standards, SAE and metric, which you need to keep in mind. However, if you just bought the socket set in different sizes, we can help you arrange them.
The most common SAE socket sizes are essential tools for any mechanic or DIY enthusiast. These sizes cover a wide range of applications, ensuring you have the right fit for various bolts and nuts.
Below, you’ll find the necessary information about metric and standard sockets, their types, measurements and sizes. You’ll also find a detailed chart for easy conversion. So, let’s begin.
Outline
ToggleMost Common Socket Sizes
Commonly used standard SAE sizes for sockets and wrenches in order:
| Socket Sizes |
|---|
| 5/16 inch. |
| 3/8 inch. |
| 7/16 inch. |
| 1/2 inch. |
| 9/16 inch. |
| 5/8 inch. |
| 11/16 inch. |
| 3/4 inch. |
| 13/16 inch. |
| 7/8 inch. |
| 1 inch. |
| 1-1/4 inch. |
| 1-7/16 inch. |
| 1-1/2 inch. |
Although there are larger sizes available, they are less common and usually reserved for specific, specialized tasks.
Now let us understand the different SAE socket sizes in detail. You can think of a drive socket as the hole (square) for attaching the socket to a turning tool like a wrench or a ratchet. There are three commonly found standard sizes according to what you need it for. Here are the details about standard socket sizes:
- 1/2″ Drives: Such drives are mostly used for heavy jobs where the nuts are massive and need more force or torque. ½” drives are mostly used in 19mm socket sizes. You can use these when driving lag bolts into the walls for mounting your LED TV.
- 3/8″ Drives: Such drives are more versatile. It’s because you can use these drives to cover sockets and areas for different jobs. It is used both at homes and workshops.
- 1/4″ Drives: When it comes to low torque jobs, you can go for 1/4″ drives. You can use such drives for small sockets with a maximum size of 14mm. It’s used for precision or interior jobs.
Different Types of Sockets
There are different sockets suited for different jobs. If you’re in the mechanical field, you’ll find the below information useful.
Here are some common types of sockets:
Impact Sockets: Most of the time, people prefer hand tools. It’s because they are old school and have a sturdy build. However, most socket types don’t attach with such tools. And this is where impact sockets come into the picture. Impact sockets are specially designed to fit in such tools.
For example, let’s suppose you’re working with a pneumatic or electric wrench. Now, for such tools, you need sockets that are sturdy and can withstand high torques. And impact sockets get the job done here as they are sturdier and more robust than conventional sockets.
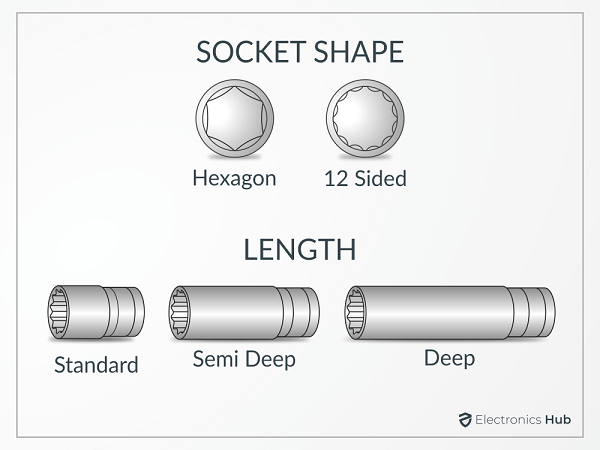
Point Sockets: Next on our list are the point sockets. Such sockets, especially the 12-point one, are very easy to fit and use. You can easily slip this socket over the tool in any of the available 12 positions. So, even if you’re a newbie, you can easily use it, as there won’t be an alignment problem.
The 12-point sockets are usually meant for light household tasks. However, there’s another category to this socket known as a 6-point socket. The 6-point socket is used for heavy jobs that require the application of heavy or substantial torque.
In such cases, the 6-point sockets are less likely to slip or move. They are considered more durable and sturdier than the inner walls. So, if you need a socket for lightweight jobs, go for the 12-point socket. Otherwise, go for a 6-point socket.
Shallow vs. Deep Sockets
The shallow socket is the other name for a normal socket. In some cases, it might not touch the nut before the bolt hits the end of the socket, which makes the job hard and sometimes not doable. In such cases, mechanics use deep sockets.
Usually, measuring one inch in length, you can use deep sockets in inaccessible places. You can do this only if your driver has an extension.
Video On Metric And Standard Socket Wrench Sizes:
Metric Socket Sizes Chart
Here are the metric socket sizes and measurements:
| 3/8″ Drive | 1/4″ Drive | 3/4″ Drive | 1/2″ Drive |
| 5.5mm | 4mm | 19mm | 8mm |
| 6mm | 4.5mm | 20mm | 9mm |
| 7mm | 5mm | 21mm | 10mm |
| 8mm | 5.5mm | 22mm | 11mm |
| 9mm | 6mm | 23mm | 12mm |
| 10mm | 7mm | 24mm | 13mm |
| 11mm | 8mm | 25mm | 14mm |
| 12mm | 9mm | 26mm | 15mm |
| 13mm | 10mm | 27mm | 16mm |
| 14mm | 11mm | 28mm | 17mm |
| 15mm | 12mm | 29mm | 18mm |
| 16mm | 13mm | 30mm | 19mm |
| 17mm | 14mm | 31mm | 20mm |
| 18mm | 15mm | 32mm | 21mm |
| 19mm | 33mm | 22mm | |
| 20mm | 34mm | 23mm | |
| 21mm | 35mm | 24mm | |
| 22mm | 36mm | 25mm | |
| 38mm | 26mm | ||
| 40mm | 27mm | ||
| 41mm | 28mm | ||
| 42mm | 30mm |
Standard SAE Socket Sizes Chart
SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) is a common system based on fractions of an inch. Standard SAE sizes include ⅜ inch, ½ inch, 9/16 inch, etc. SAE is the more widely used term for these fractional inch socket sizes in order.
Here is the standard SAE socket size chart:
| 3/8″ Drive | 1/4″ Drive | 3/4″ Drive | 1/2″ Drive |
| 1/4″ | 5/32″ | 7/8″ | 3/8″ |
| 5/16″ | 3/16″ | 15/16″ | 7/16″ |
| 3/8″ | 7/32″ | 1″ | 1/2″ |
| 7/16″ | 1/4″ | 1-1/16″ | 9/16″ |
| 1/2″ | 9/32″ | 1-1/8″ | 19/32″ |
| 9/16″ | 5/16″ | 1-3/16″ | 5/8″ |
| 5/8″ | 11/32″ | 1-1/4″ | 21/32″ |
| 11/16″ | 3/8″ | 1-5/16″ | 11/16″ |
| 3/4″ | 7/16″ | 1-3/8″ | 3/4″ |
| 13/16″ | 1/2″ | 1-7/16″ | 25/32″ |
| 7/8″ | 9/16″ | 1-1/2″ | 13/16″ |
| 15/16″ | 1-5/8″ | 7/8″ | |
| 1″ | 1-11/16″ | 15/16″ | |
| 1-3/4″ | 1″ | ||
| 1-13/16″ | 1-1/16″ | ||
| 1-7/8″ | 1-1/8″ | ||
| 2″ | 1-3/16″ | ||
| 2-1/8″ | 1-1/4″ | ||
| 2-3/16″ | 1-1/2″ | ||
| 2-1/4″ |
Standard Socket Sizes Conversion
Standard Socket Size is more general term and less widely used. SAE Size and Standard Socket Size both use the same inch system for measurement, so you can refer the Standard Socket Sizes to SAE sizes. However, it can also include other inch-based sizing systems that aren’t strictly SAE. If you are not sure about a socket set sizes, it’s usually safe to assume it uses SAE sizes.
| SAE Size | Metric Size | Inches Decimal | |
| 5/32″ | 0.156 | 5/32″ and 4mm are | |
| 4mm | 0.157 | close enough | |
| 4.5mm | 0.177 | ||
| 3/16″ | 0.188 | ||
| 5mm | 0.197 | ||
| 5.5mm | 0.216 | ||
| 7/32″ | 0.219 | ||
| 6mm | 0.236 | ||
| 1/4″ | 0.25 | ||
| 6.5mm | 0.256 | ||
| 7mm | 0.276 | ||
| 9/32″ | 0.281 | ||
| 5/16″ | 0.313 | 5/16″ and 8mm are | |
| 8mm | 0.315 | close enough | |
| 11/32″ | 0.344 | ||
| 9mm | 0.354 | ||
| 3/8″ | 0.375 | ||
| 10mm | 0.394 | ||
| 13/32″ | 0.406 | ||
| 11mm | 0.433 | 7/16″ and 11mm are | |
| 7/16″ | 0.438 | close enough | |
| 15/32″ | 0.469 | 15/32″ and 12mm are | |
| 12mm | 0.472 | close enough | |
| 1/2″ | 0.5 | ||
| 13mm | 0.512 | ||
| 17/32″ | 0.531 | ||
| 14mm | 0.551 | ||
| 9/16″ | 0.563 | ||
| 15mm | 0.591 | 19/32″ and 15mm are | |
| 19/32″ | 0.594 | close enough | |
| 5/8″ | 0.625 | ||
| 16mm | 0.63 | ||
| 21/32″ | 0.656 | ||
| 17mm | 0.669 | ||
| 11/16″ | 0.688 | ||
| 18mm | 0.709 | ||
| 23/32″ | 0.719 | ||
| 19mm | 0.748 | 3/4″ and 19mm are | |
| 3/4″ | 0.75 | close enough | |
| 25/32″ | 0.781 | ||
| 20mm | 0.787 | ||
| 13/16″ | 0.813 | ||
| 21mm | 0.827 | ||
| 27/32″ | 0.844 | ||
| 22mm | 0.866 | ||
| 7/8″ | 0.875 | ||
| 23mm | 0.906 | 29/32″ and 23mm are | |
| 29/32″ | 0.906 | close enough | |
| 15/16″ | 0.938 | ||
| 24mm | 0.945 | ||
| 1″ | 1 |
SAE To Imperial Socket Sizes Conversion:
SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) is a subset of the imperial measurement system that uses fractions of an inch for fasteners. Both SAE and imperial measurements are part of the same system, but SAE specifically utilizes fractional inch sizes, which can sometimes necessitate conversion to the more globally common metric system, measured in millimeters.
SAE To Metric Socket Conversion Chart
Sometimes when you have a wrench in the metric units and a nut in Imperial units, you would not know whether it’ll fit or not. In such cases, you need to know how to correctly convert one unit into another. And the below chart will help you easily convert the dimensions from SAE to Metric or vice versa.
Conversion Formula:
SAE to Metric:
- Multiply the SAE size (in inches) by 25.4 to convert it to millimeters.
- Example: 3/8″ * 25.4 = 9.525mm (approximately 10mm).
Metric to SAE:
- Multiply the metric size (in millimeters) by 0.03937 to convert it to inches.
- Example: 10mm * 0.03937 = 0.3937″ (approximately 3/8″).
| SAE (Inches) | Metric (Millimeters) |
|---|---|
| 1/4″ | 6.35mm |
| 5/16″ | 7.94mm |
| 3/8″ | 9.53mm |
| 7/16″ | 11.11mm |
| 1/2″ | 12.70mm |
| 9/16″ | 14.29mm |
| 5/8″ | 15.88mm |
| 11/16″ | 17.46mm |
| 3/4″ | 19.05mm |
| 13/16″ | 20.64mm |
| 7/8″ | 22.23mm |
| 1″ | 25.40mm |
Socket Wrench Size Chart
Wrench Size chart lists both metric and standard socket wrench sizes in order from smallest to largest. The bolt diameter is the distance between the two prongs of the wrench. Use this measurement to find compatible nut and bolt sizes.
| Bolt Diameter | Metric | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| 1/8″ | 8mm | 5/16″ |
| 3/16″ | 10mm | 3/8″ |
| 1/4″ | 11mm | 7/16″ |
| 5/16″ | 13mm | 1/2″ |
| 3/8″ | 14mm | 9/16″ |
| 7/16″ | 16mm | 5/8″ |
| 1/2″ | 19mm | 3/4″ |
| 9/16″ | 21mm | 13/16″ |
| 22mm | 7/8″ | |
| 5/8″ | 24mm | 15/16″ |
| 25mm | 1″ | |
| 3/4″ | 29mm | 1-1/8″ |
| 32mm | 1-1/4″ | |
| 7/8″ | 34mm | 1-5/16″ |
| 35mm | 1-3/8″ | |
| 1″ | 38mm | 1-1/2″ |
| 41mm | 1-5/8″ | |
| 1-1/8″ | 43mm | 1-11/16″ |
| 45mm | 1-3/4″ | |
| 1-1/4″ | 48mm | 1-7/8″ |
| 1-3/8″ | 51mm | 2″ |
| 1-1/2″ | 57mm | 2-1/4″ |
| 1-5/8″ | 64mm | 2-1/2″ |
| 1-3/4″ | 67mm | 2-5/8″ |
| 70mm | 2-3/4″ | |
| 1-7/8″ | 75mm | 2-15/16″ |
| 76mm | 3″ | |
| 2″ | 80mm | 3-1/8″ |
| 83mm | 3-1/4″ | |
| 2-1/4″ | 89mm | 3-1/2″ |
| 95mm | 3-3/4″ | |
| 2-1/2″ | 99mm | 3-7/8″ |
| 102mm | 4″ | |
| 2-3/4″ | 108mm | 4-1/4″ |
| 114mm | 4-1/2″ | |
| 3″ | 118mm | 4-5/8″ |
| 3-1/4″ | 127mm | 5″ |
| 3-1/2″ | 137mm | 5-3/8″ |
| 140mm | 5-1/2″ | |
| 3-3/4″ | 146mm | 5-3/4″ |
| 152mm | 6″ | |
| 165mm | 6-1/2″ | |
| 178mm | 7″ |
SAE Socket Sizes Chart – FAQs
1. What socket sizes are required for my task?
Select the drive size of ratchets and sockets based on the diameter of the bolt or nut. For fasteners around 1/4″ or 6mm, use the 1/4″ drive. For hardware approximately 3/8″ or 10mm, choose the 3/8″ socket set.
2. What is the typical use or purpose of a standard SAE socket size?
The standard socket size is determined by the opening on a socket wrench, designed to fit a specific nut or bolt size. Common sizes include 1/4 inch, 3/8 inch, 1/2 inch, 3/4 inch, and 1 inch, with additional sizes available for specialized applications.
3. What socket size is typically required for lug nuts?
For lug nuts, the most common socket sizes are 17 mm, 19 mm, 21 mm, and 22 mm in metric, as well as 11/16-inch, 3/4-inch, 13/16-inch, and 7/8-inch in SAE. These sizes can be found at Olsa Tools.
4. Which socket is typically required for changing a tire?
To change a tire, you typically use a lug wrench, which is a type of socket wrench, to loosen the lug nuts. Ensure you follow proper safety precautions and use the correct tools for the job.
Conclusion
Being a mechanic is a tough job. And if you’re dealing with a socket set or socket organizer, the job becomes even harder. There are different sizes, types, and even measurement units for sockets. And without adequate information, everything could sound gibberish.
However, the above information is enough to enlighten you. We have discussed the sizes of drives and types of sockets. You can check the size of sockets in the metric as well as in the SAE system. Also, you can find a conversion chart for converting the sizes into the desired unit type. This way, you can sort the sockets the way you want and save some time while doing the job.


6 Responses
Very very helpful excellent job
Thank you so much, now I’ll have fun organizing my tools lol.
Wonderful video & information chart
Thank you for being so helpful and simplistic.
Can I use star key like L-keys
Great job learned a lot