The CPU or the processor of your desktop or laptop is one of the most important internal components. Since it handles all of your tasks and applications, having a powerful CPU is highly important. This becomes even more important if you are running CPU intensive tasks on your computer. Even if your computer has a powerful CPU inside, making sure that it is performing optimally is very important. And while you can use the Task Manager in Windows to check the basic parameters of your CPU such as its clock speed and percentage of utilization, it shows very limited details. If you want to know more about your CPU, its performance numbers, and detailed specifications, then you may want to use a third-party software. While there are several third-party system monitoring applications, the one we are going to talk about is Quick CPU. It is a unique piece of software in the sense that you can not only monitor system parameters but also tweak them if necessary.
Today, we are here with a complete overview of Quick CPU which will take you through all of its details to help you understand the benefits offered by it and why you should install Quick CPU on your PC. Before proceeding further, we would like to stress that if you want to change any parameters (such as clock speed, power limits, etc.) of your CPU, then you have to do it at your own risk. This is just a guide explaining the features of the Quick CPU application and is not a user guide on how to use it.
Outline
ToggleWhat is Quick CPU?
System monitoring software is a category of software applications designed to observe, analyze, and report on the performance and health of computer systems and networks. Performance Monitoring is a primary function of system monitoring software. It continuously tracks the performance of critical system resources such as the CPU, memory, disk drives, and network interfaces. This data helps users identify bottlenecks and resource constraints while enabling efficient resource allocation and capacity planning.
Quick CPU is a free and open-source software utility for Windows that allows users to monitor and adjust various CPU and system parameters to optimize performance and power management. It provides a wealth of information about the CPU, including its temperature, frequency, voltage, power consumption, and more. Users can also use Quick CPU to adjust the CPU’s frequency, voltage, and power limits. It can be useful for enthusiasts and advanced users who want to fine-tune their CPU settings.
Since it is a monitoring application, it also shows you the real-time usage of your processor and its performance numbers. Unlike Windows Task Manager, Quick CPU offers much more detail in terms of CPU usage, core usage, CPU temperature, core temperature, TDP or power consumption, cache details, and much more regarding your CPU in both numbers as well as graphs.
Quick CPU is a powerful tool that can be used to improve the performance of your computer. However, it is important to use it with caution, as overclocking the CPU can damage it if done incorrectly.
Quick CPU: Features and Functions
Even though we have already discussed an overview of Quick CPU and what it offers to the user, there is still a lot to consider before you go ahead and install Quick CPU. This primarily includes the various features and functions offered by Quick CPU which are as follows:
- Monitoring: Quick CPU provides a real-time view of the CPU’s temperature, frequency, voltage, power consumption, and other metrics.
- Fine-tuning: Quick CPU allows users to adjust the CPU’s frequency, voltage, and power limits.
- CPU Presets: Quick CPU provides three preset performance modes: Minimum, Balanced, and Maximum.
- Data Logging: Quick CPU can log the CPU’s performance data to a file.
- Benchmarking: Quick CPU can benchmark the CPU’s performance.
- Others
- Performance graphs/plots for all CPU cores for checking their current consumption and utilizations.
- Ability to adjust CPU consumption graphs in terms of their size.
- Real time core counter for checking active and parked cores.
- Adjustable CPU core parking, frequency scaling, and turbo boost settings.
- Real time C-State Residency, CPU speed, CPU utilization, and CPU temperature details.
- System memory profile, power output, and power plan options.
- Regular application updates for more features and bug fixes.
Quick CPU is a free and open-source software utility that is available for download from the CoderBag website.
How to Use Quick CPU?
In addition to exploring the features and available options within Quick CPU, it is essential to understand how to effectively utilize this tool. The reason is simple: without proper knowledge of Quick CPU’s usage, you won’t be able to harness its full potential. This aspect becomes even more crucial if you are a newcomer to computer hardware monitoring programs. Fortunately, the process of using Quick CPU is straightforward, thanks to its organized layout, where all of its features are conveniently categorized into distinct sections, as outlined below:
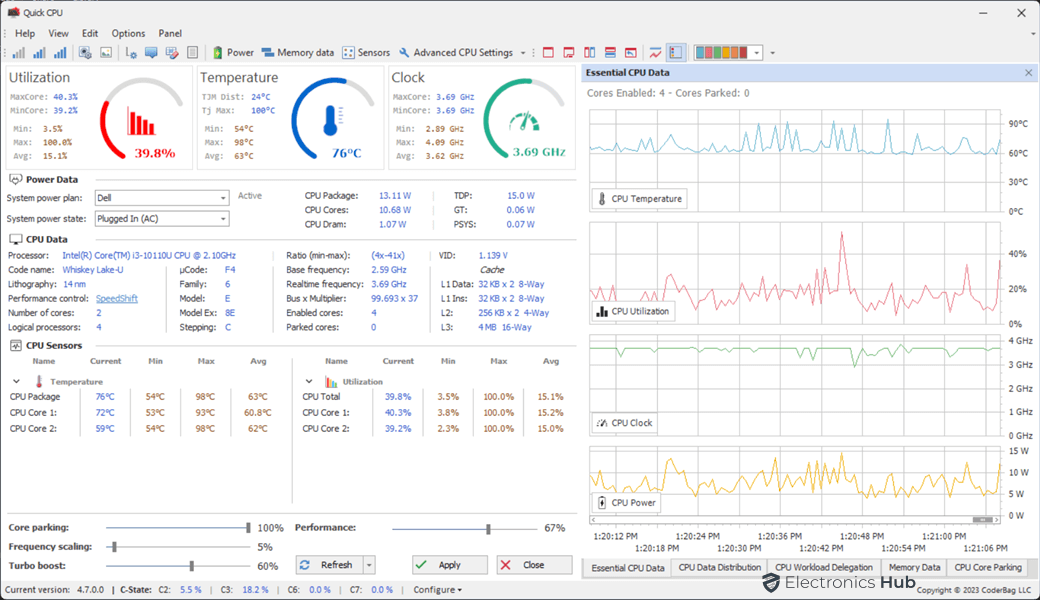
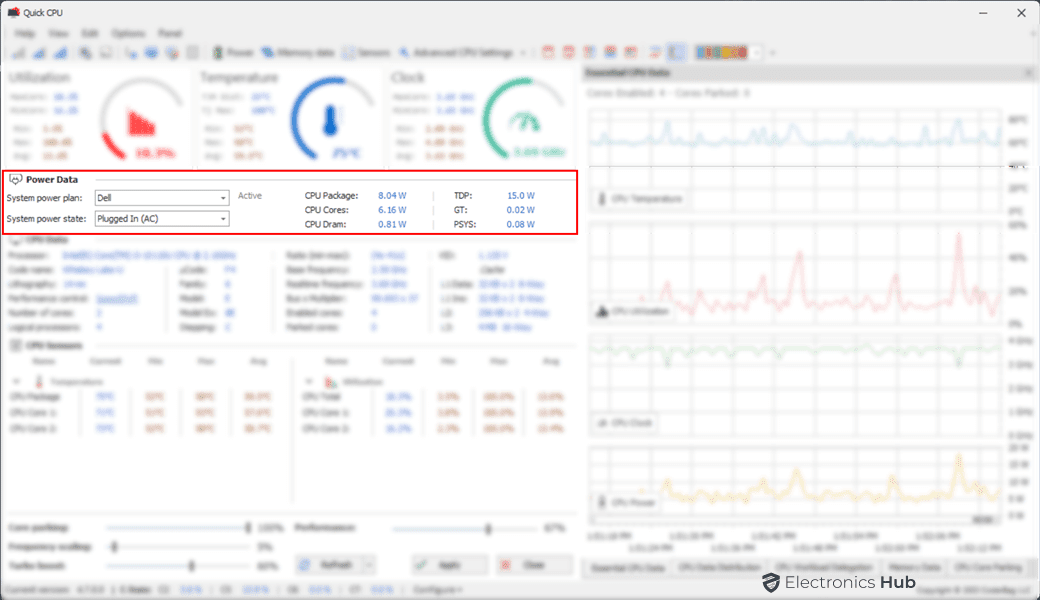
Power Data
This section provides information about your computer’s power consumption, including the current power plan, charging status (for laptops), power draw by the entire CPU Package, power draw of cores, and TDP rating. You can also use this section to change the system power plan and power state.
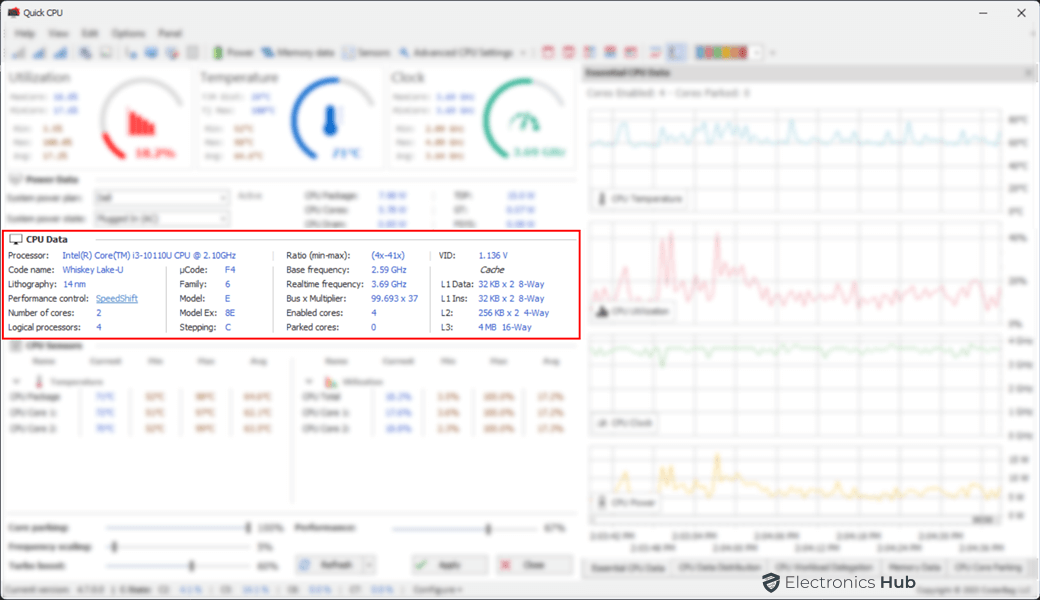
CPU Data
The CPU Data section is an invaluable resource, especially if you’re seeking detailed information about the processor within your computer. Within this section, you’ll find a comprehensive overview of your processor, including its name, codename, lithography, socket type, core count, logical processors, base frequency, real-time frequency, bus multiplier, enabled cores, parked cores, CPU voltage, and cache details encompassing L1, L2, and L3 caches.
All the data within this area is strictly for viewing purposes, and no interaction is possible. This feature enables you to effortlessly access and verify the specifications and important details of your CPU, including its model number and manufacturing specifics, including the CPU ID.
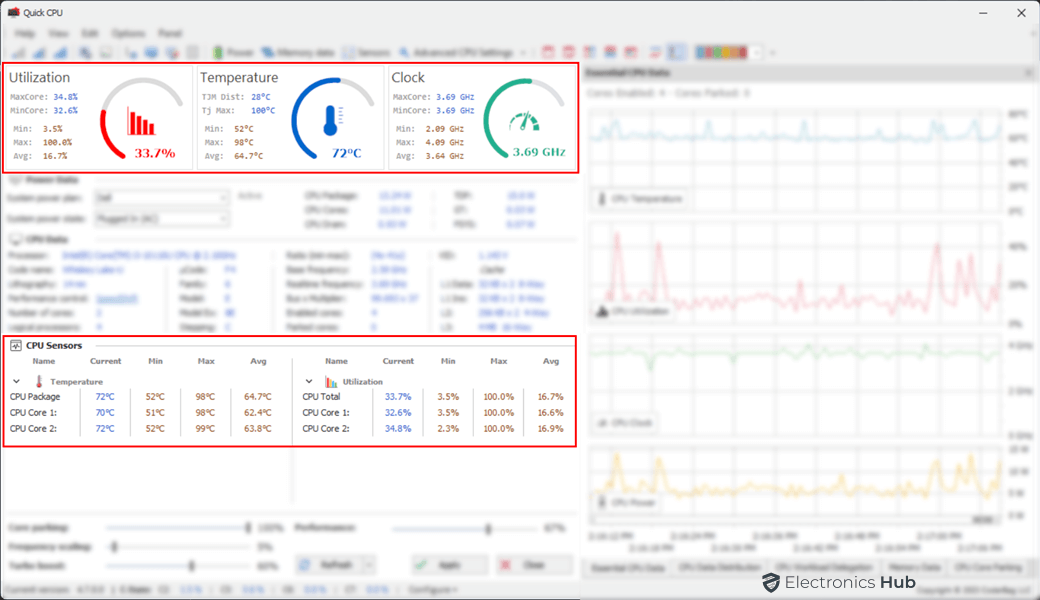
CPU Utilization, Temperature, and Clock
These sections provide you with comprehensive insights into your computer’s CPU performance. Here, you can monitor real-time CPU usage, including current, minimum, and maximum utilization for both the overall CPU package and individual cores. While CPU utilization should be plenty to check for most users, advanced users may also want to check the real-time clock speed of the CPU. You can also use this information to troubleshoot problems with overclocking.
In addition to CPU utilization, this section offers a detailed view of processor temperatures, ensuring that your CPU is adequately cooled and not experiencing thermal throttling. You can track the temperature of the processor package and each individual core.
CPU Core Parking
CPU Core Parking is a feature in Windows (introduced with Windows Server 2008 R2) that allows the operating system (the combination of processor power management (PPM) engine and scheduler) to dynamically adjust the number of CPU cores that are available to run threads. This can help to save power when the computer is not under heavy load. However, the default settings for CPU Core Parking in Windows are not very flexible.
Quick CPU allows you to control the number of CPU cores that are enabled or disabled. This can be useful for users who want to improve the performance of their computer or who want to save more power. It also provides real-time information about which CPU cores are enabled and disabled. This information can be useful for troubleshooting problems or for understanding the performance of your computer.
Here are some of the benefits of using Quick CPU to control CPU Core Parking:
- Reduced power consumption: By disabling unused CPU cores, Quick CPU can save power. This can be especially beneficial for laptops and other mobile devices.
- More flexibility: Quick CPU provides a variety of options for controlling CPU Core Parking. This gives users more control over how their computer uses power and resources.
Frequency Scaling
CPU frequency scaling is a feature that allows the operating system to adjust the CPU’s frequency up or down, depending on the workload. This can help to improve performance when the CPU is needed and save power when it is not.
The CPU frequency scaling index works in a similar way to the CPU core parking index. When the index is set to 100%, the CPU will run at its base frequency. However, the CPU can still boost its frequency above the base level if needed, thanks to Intel Turbo Boost or AMD Turbo CORE technologies. Here is an example of how CPU frequency scaling works:
- If the CPU frequency scaling index is set to 100% and the system is under light load, the CPU will run at its base frequency.
- If the system load increases, the CPU frequency scaling index will also increase. This will cause the CPU to run at a higher frequency, which can improve performance.
- The other case is also true. If the system load decreases, the CPU frequency scaling index will decrease. This will cause the CPU to run at a lower frequency, which can save power.
It is important to note that CPU frequency scaling is a complex topic, and there are many other factors that can affect the CPU’s frequency (for example, the CPU temperature and the power consumption).
Set CPU Performance
Quick CPU provides three preset performance profiles: Minimum, Balanced, and Maximum. You can select these profiles from the three graph icons at the top of the Quick CPU window (or from the “Options” tab).
- Minimum Performance profile is designed to save power. It will reduce the CPU frequency and voltage, which will reduce performance but also save battery life.
- Balanced Performance profile is designed to be a compromise between performance and power consumption. It will adjust the CPU frequency and voltage based on the system load.
- Maximum Performance profile is designed to maximize performance. It will set the CPU frequency and voltage to their highest levels, which can improve performance but also increase power consumption and heat generation.
Which performance profile is best for you will depend on your individual needs and preferences. If you are looking to save battery life, you should use the Minimum Performance profile. If you are looking for a good balance between performance and power consumption, you should use the Balanced Performance profile. And if you need the absolute best performance, you should use the Maximum Performance profile.
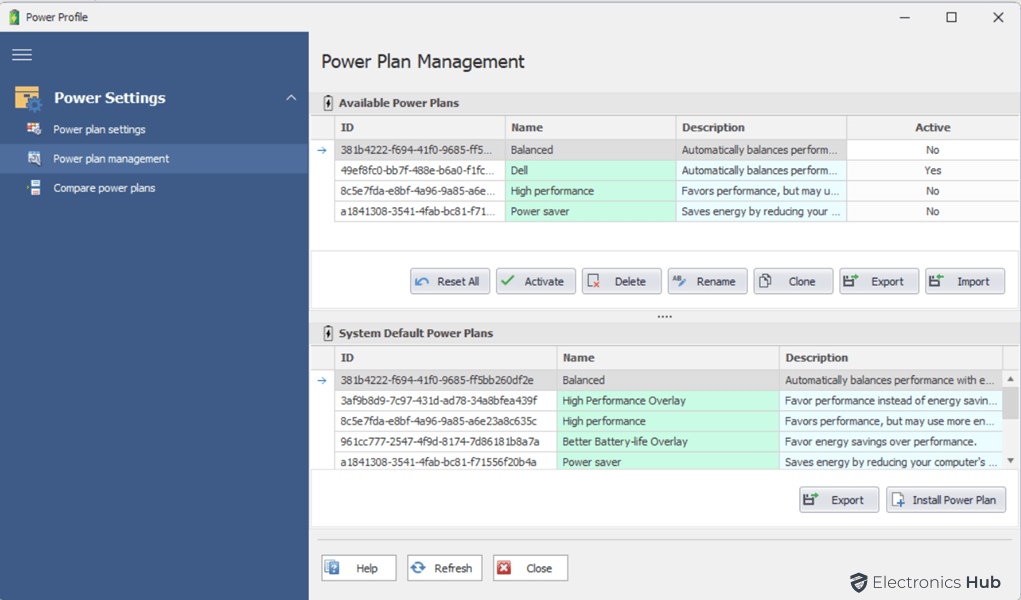
Power Plan Management
Quick CPU’s Power Plan Management feature allows users to view, modify, and manage Windows power plans. This feature is more powerful and flexible than the built-in power plan management features in Windows 10.
To access the Power Plan Management feature, click the “Power” button at the top of the Quick CPU window. This will open a new window with the following three sections:
- Power Plan Settings: This section allows users to view, describe, and modify the power plan settings for the selected power plan.
- Power Plan Management: This section allows users to manage the power plans themselves, including editing, importing, exporting, activating, deleting, cloning, and resetting power plans.
- Compare Power Plans: This section allows users to compare and merge the power setting values (AC/DC) for two different power plans.
To use the Power Plan Management feature, simply click on the button for the action you want to perform. For example, to change your power plan, click the “Change Power Plan” button. To create a new power plan, click the “Create New Power Plan” button. To compare two power plans, click the “Compare Power Plans” button.
The Power Plan Management feature is a powerful tool that can be used to optimize your computer’s performance and power consumption. It is a valuable addition to the Quick CPU software utility.
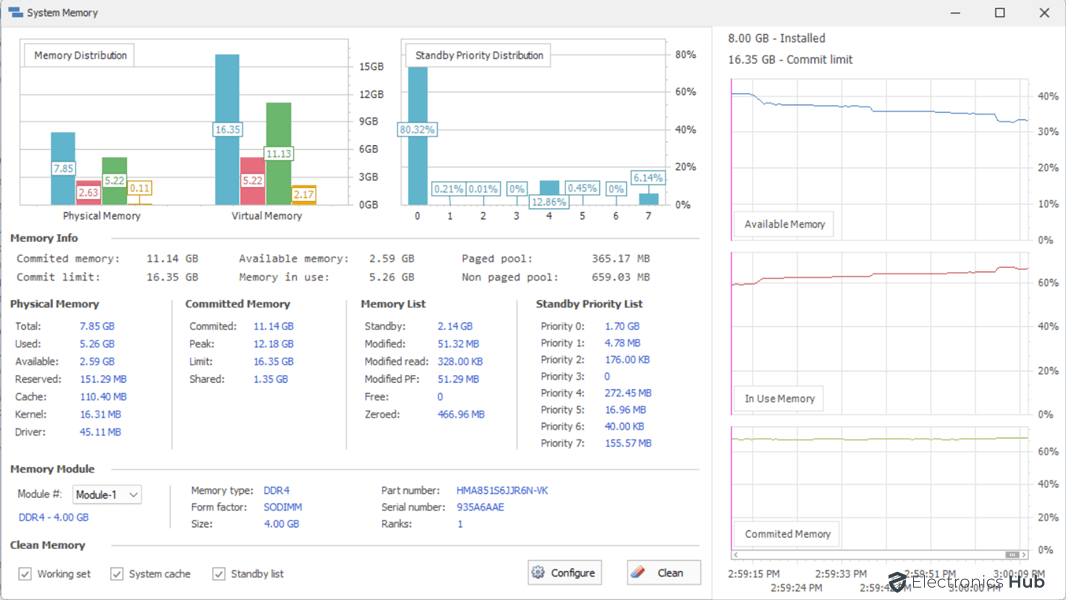
Memory Data
The Memory Data section of Quick CPU provides information about your computer’s memory usage. This information can be useful for troubleshooting problems or for understanding how your computer is using memory.
To access the Memory Data section, click the “Memory” button at the top of the Quick CPU window. This will open a new window with the following information:
- Memory in Use: This is the amount of memory that is currently being used by programs and services.
- Committed Memory: This is the amount of memory that has been allocated to programs and services, even if they are not currently using it.
- Available Memory: This is the amount of memory that is currently available for use by programs and services.
You can view this information as raw numbers as well as percentages. The Memory Data section can be used to identify programs or services that are using a lot of memory. If you see that a program or service is using more memory than you expected, you can try closing it or reducing its memory usage.
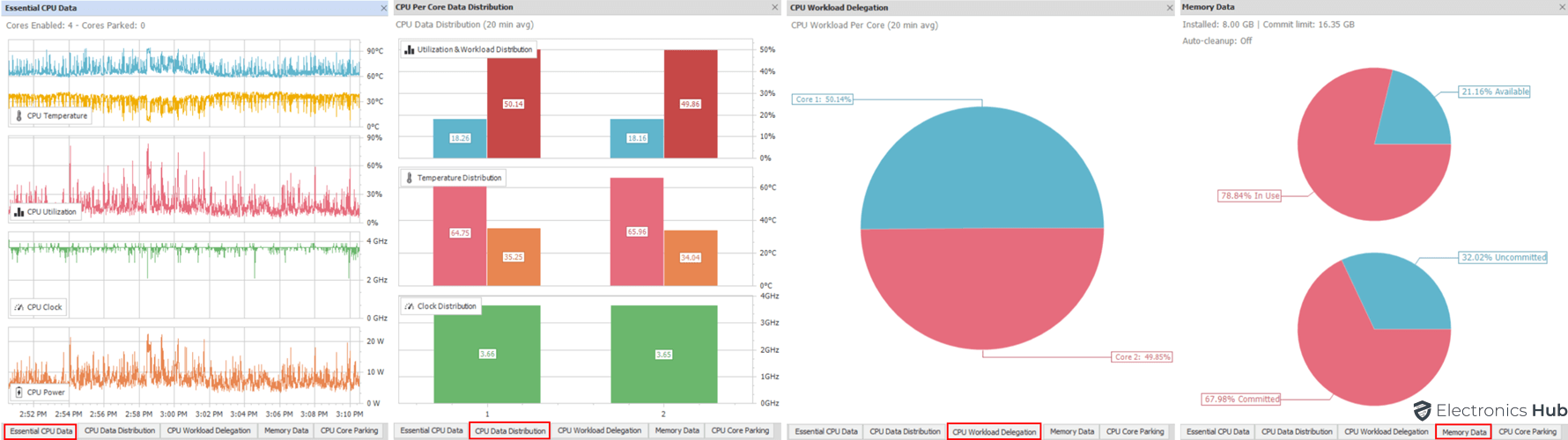
Quick CPU Charts
Quick CPU also provides a variety of charts that can be used to visualize this data.
- The Essential CPU Data Chart Panel shows five different CPU indicators: CPU temperature, CPU temperature for distance to Tj Max (available for Intel and AMD Ryzen CPUs), CPU load, CPU clock speed, and CPU power. This chart can be used to monitor the CPU’s performance and to identify any potential problems.
- CPU Data Distribution Chart Panel shows how evenly the CPU’s load, temperature, clock frequency, and power are distributed among all of the CPU cores. This information can be used to identify any cores that are overloaded or underutilized.
- The CPU Workload Delegation Chart Panel shows how the operating system is delegating workload to each of the CPU cores. This information can be used to understand how the operating system is using the CPU’s resources and to identify any performance bottlenecks.
- Memory Data Chart Panel shows two charts that show memory usage data: available vs. used memory and committed vs. uncommitted memory. This information can be used to monitor memory usage and to identify any potential memory problems.
Quick CPU Advanced CPU Settings
Another useful feature of Quick CPU is its Advanced CPU Settings that allows users to modify advanced CPU settings. These settings are not intended for general users and should only be modified by users who have a clear understanding of their functionality. Modifying these settings can potentially void your CPU warranty.
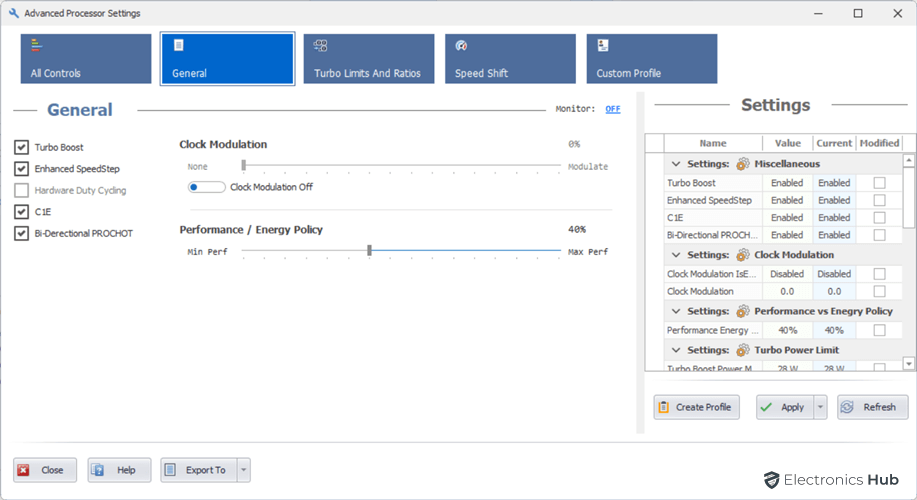
General Settings
The General Settings in Quick CPU are a set of CPU settings that can be used to improve performance, reduce power consumption, and extend battery life. These settings are CPU dependent and may not be available on all CPUs.
- Turbo Boost: It is a technology that allows the CPU to run at higher frequencies than its base frequency when the system has the thermal and power headroom. This can improve performance for demanding tasks, such as gaming and video editing.
- Enhanced SpeedStep: This technology allows the CPU to adjust its frequency and voltage based on the workload. This can help to save power and reduce heat generation.
- Hardware Duty Cycling (HDC): HDC is a power saving feature that allows the CPU to disable unused cores and reduce its frequency. This can help to save power when the system is under light load.
- C1E: This is a power saving feature that allows the CPU to enter a low-power state when it is idle. This can help to improve battery life.
- Bi-Directional PROCHOT: This feature allows the CPU to communicate with other components in the system, such as the motherboard and GPU. This can help to improve thermal management and power consumption.
- Clock Modulation: Clock modulation is a feature that allows the CPU to reduce its frequency and voltage. This can help to save power and reduce heat generation.
- Performance / Energy policy: The Performance / Energy policy allows the user to choose between prioritizing performance or power conservation.
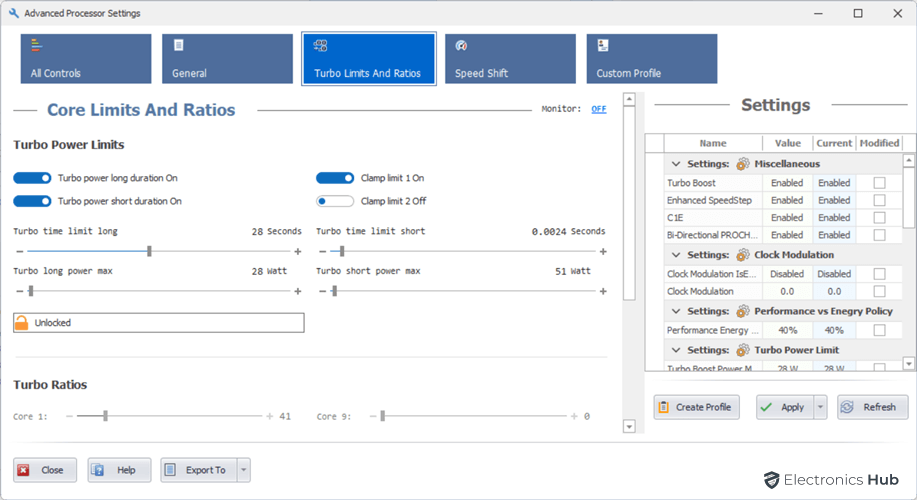
Turbo Limits
Turbo Power Limits (TPLs) are a set of settings that allow you to control how your CPU consumes power. These settings are especially useful for laptops and other mobile devices, where power consumption is a major concern.
There are two main TPL settings:
- Power Limit Long (PL1): This setting defines the maximum power that the CPU can consume for sustained periods of time.
- Power Limit Short (PL2): This setting defines the maximum power that the CPU can consume for short periods of time, such as when under heavy load.
In addition to the power limits, there are also two timing variables associated with each power limit:
- Time Limit Long: This setting defines the maximum amount of time that the CPU can spend in PL1 mode.
- Time Limit Short: This setting defines the maximum amount of time that the CPU can spend in PL2 mode.
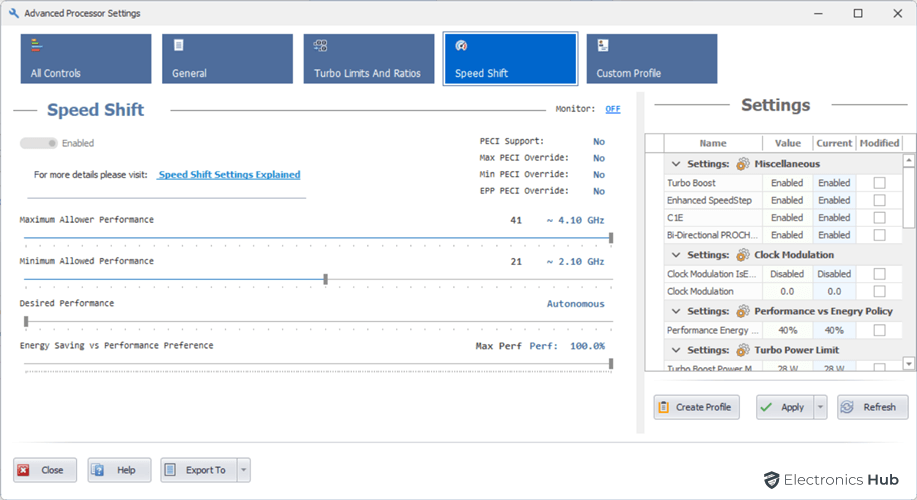
Speed Shift Technology
Intel’s Speed Shift technology allows the CPU to more quickly select its best operating frequency and voltage for optimal performance and power efficiency. It works by allowing the CPU to take over responsibility for frequency control from the operating system. This results in much faster p-state transitions, which can drastically reduce latency during the process of p-state selection.
This is especially useful for laptops and other mobile devices, where power consumption is a major concern. By allowing the CPU to more quickly select its best operating frequency and voltage, Speed Shift can help to improve battery life and reduce heat generation.
How to Use Speed Shift in Quick CPU?
Speed Shift can be enabled in the BIOS or UEFI settings on most modern Intel CPUs. Once Speed Shift is enabled, you can adjust the Speed Shift performance settings in Quick CPU. The Speed Shift performance settings include:
- Maximum Allowed Performance: Specifies the maximum clock frequency that the CPU can operate at.
- Minimum allowed performance: Specifies the minimum clock frequency that the CPU can operate at.
- Desired Performance: Specifies the desired performance level. When set to zero, the hardware automatically determines the performance target. When set to a non-zero value, it specifies an explicit performance request hint to the hardware.
- Energy Saving vs Performance Preference: Specifies a preference for energy efficiency over performance. A value of zero indicates a preference for performance, while a value of 255 indicates a preference for energy efficiency.
Quick CPU: System Requirements and Specifications
Now that you know more about Quick CPU and the benefits of using this application on your computer, you might want to install Quick CPU on your PC right away. Before doing so, it is highly important to ensure that Quick CPU is compatible with your PC and its specifications. One easy way to ensure the same is to simply check the system requirements of Quick CPU. You can simply go through the following and see if your computer offers the same or better specs:
- Compatible Operating System: Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7
- Minimum System Memory/RAM: 2 GB RAM minimum, 4 GB RAM recommended
- Required Hard Disk Space: 200 MB or more
Conclusion
Quick CPU is a versatile and comprehensive software tool that allows users to monitor and adjust critical CPU parameters, such as core activation, core parking, and frequency scaling. With this level of control, users can optimize system performance, manage power consumption, and ensure efficient resource allocation. Quick CPU is a valuable tool for a variety of users, including seasoned computer enthusiasts, novice users, and system administrators. Seasoned computer enthusiasts can use Quick CPU to fine-tune CPU settings to achieve peak performance for gaming, video editing, and other demanding tasks. Novice users can use Quick CPU to understand and improve system performance without the need for deep technical knowledge. System administrators can use Quick CPU to optimize CPU settings for multiple systems in a network environment.
Overall, Quick CPU is a valuable tool for users seeking to improve system performance, reduce power consumption, and enhance CPU customization. It is a versatile and accessible solution for both experienced and novice users alike.
FAQs
What is Quick CPU, and what does it do?
Answer: Quick CPU is a software utility designed to monitor and adjust various CPU and system parameters. It allows users to control core activation, core parking, frequency scaling, and more to optimize CPU performance and power management.
Is Quick CPU a free software tool, or does it require a purchase?
Answer: Quick CPU, developed by Coder Bag for Windows, is a completely free software. You can use it to fine-tune and monitor critical computer system parameters.
Is Quick CPU compatible with all CPU types and operating systems?
Answer: Quick CPU primarily targets Windows-based systems and works with both Intel and AMD CPUs. Compatibility may vary depending on the specific hardware and software configurations.
Is it safe to use Quick CPU to modify CPU settings?
Answer: While Quick CPU provides powerful tools for adjusting CPU settings, users should exercise caution. Incorrect settings can potentially harm your system or void warranties. Users have to understand the changes they’re making and their potential impact.
Can Quick CPU help with overclocking my CPU for better performance?
Answer: Yes, Quick CPU can assist with CPU overclocking by allowing users to adjust clock frequencies and other performance-related settings. However, overclocking carries certain risks, including increased heat generation, so users should be knowledgeable about the process.