Welding is a process of fusing two separate material pieces with heat and pressure. During the welding process, a soft joint forms, which cools down to become a strong and hardened joint. There are different types of welding techniques that professionals use depending on the materials and their specifications.
Arc welding is the most popular welding technique used in the industry. And it consists of many sub-techniques such as Metal Inert Gas(MIG) and Tungsten Inert Gas(TIG). In this article, we have given an in-depth explanation of both MIG and TIG welding along with their benefits, applications, similarities, and differences. So if you were curious to learn more, stick to the very end.
Outline
ToggleMIG Welding
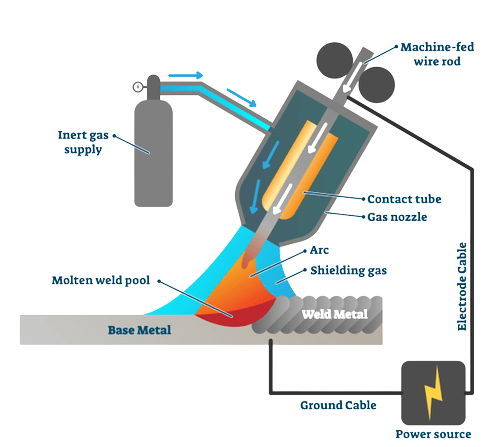
In MIG welding, you need a workpiece containing the base metal and a wire electrode containing the filler material. The base metal is welded, and the filler material is deposited to form a strong joint in the welded area.
In the welding machine, you have to feed the wire electrode from a wire reel—an electric arc forms in between the workpiece and the tip of the wire electrode. The arc heats up the materials and melts them, forming a weld pool. There is a need to use a shielding gas to prevent the molten weld pool from reacting with other elements present in the air.
The electrode melts and deposits in the weld joint for welding the workpiece. The entire process runs in semi-automated equipment. The welder can adjust the melting speed and deposition direction. The selection of the filler material depends on the base material that is being welded.
TIG Welding
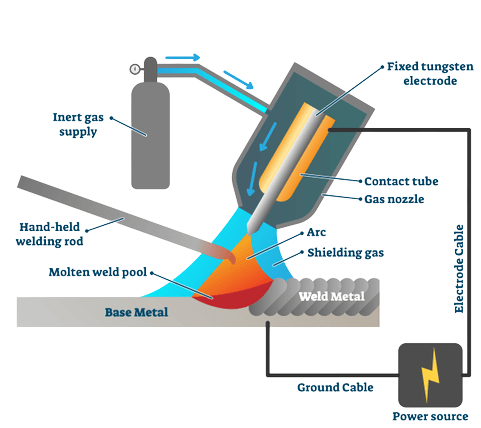
In TIG welding, you need a workpiece containing the base metal and a non-consumable electrode containing tungsten. The electric arc forms between the tungsten electrode and the base metal of the workpiece. An inert gas acts as a shielding gas in the process to prevent the molten weld pool from reacting with elements in the air.
As the tungsten electrode is infusible, you need to supply the filler material externally as a rod. Besides, the process needs a constant current power source. TIG welding is a rather manual process, and hence, the welder needs enough experience for perfection.
MIG Welding: Benefits and Applications
There are various benefits of MIG welding, which is why it is the most popular welding process used in the professional field.
- Speed – The process is semi-automatic, and hence, there are few stops and starts. Therefore, the deposition rate is high leading to the high speed of welding.
- Easy Operation – MIG welding is the easiest welding process as it is semi-automatic, and even beginners can do it without much skill.
- Versatile – The process is applicable to most of the metal, starting from steel and nickel to different metal alloys.
- Better Visibility – Most of the process is hands-free, and you get better visibility of the weld pool and weld formation. As there is less intervention, weld joints are clean and consistent.
- Greater Penetration – With a better weld pool formation due to heating and melting of materials, the materials can mix better, and the weld formation is uniform with greater penetration of the material.
Application
MIG welding is perfect for welding large and thick materials with speed and adjustability.
- Welding Pipe – Welding pipes are thick, and hence, MIG welding fits the best. All the different types of pipes for regular and industrial applications can be welded with MIG welding.
- Railways Industry – MIG welding finds a wide range of applications in railroad track building and joining. Even repairing the worn-out track and locomotive can be done with this welding process.
- Regular Repairing – MIG welding is widely used in all repairing works where welding plays a major role. As a matter of fact, it is perfect for large-scale welding, thanks to its speed.
Apart from these, from steel structure building and repairing to the automotive and home improvement industry, all rely on MIG welding.
TIG Welding: Benefits and Applications
There are various benefits of TIG welding, which is why it is the most preferred welding process by experienced welders.
- Neat Weld Joint – Out of all the welding techniques, TIG welding ensures the best result as the final output is neat, clean, and precise. Therefore, the appearance of the weld joint is going to be far better than any other process. It is highly useful in the professional field where the joint should not disturb the aesthetic value of the object.
- Compatibility and Durability – TIG welding is applicable on a variety of metals, starting from aluminum and magnesium to steel, nickel, copper, and even gold. As far as durability is concerned, TIG weld joints are surely highly long-lasting, which is always desirable.
- All Position Welding – TIG welding lets the welders weld the base metal in any position. Whether it is flat, horizontal, vertical, or overhead position, you can weld it in any confined area without any issue.
- Clean Process – There is no spark and spatter generated in the process. This is because there is no extra consumption of filler material, and you only add the filter material when needed. As a matter of fact, the process does not generate too much smoke or fume if the base metal is clean. Moreover, this process doesn’t require flux or slag.
- One Shielding Gas – There is no need for scratching your head about which shielding gas to be used based on filler material or base metal. This is because one shielding gas is enough for all applications, which happens to be Argon.
Application
TIG welding is perfect for welding small and thin materials with precision and accuracy.
- Automotive Industry – As the weld joints are neat and clean, TIG welding finds a wide range of applications in the automotive industry. Moreover, the joints are strong and durable, and they do not break due to regular wear and tear.
- Aerospace Industry – As the weld joints can be done precisely with TIG welding, the aerospace industry relies on it for all welding jobs. Apart from strength, the aesthetic value is also taken care of in TIG welding. Besides, aerospace projects involve the usage of the aluminum body where TIG welding acts the best.
- Manufacturing Industry – TIG welding finds a considerable application in the manufacturing industry, especially in areas where welder does not get much space for welding. Apart from that, regular repairing can also be done where durability is the priority.
Similarities between MIG and TIG welding –
There are only a handful of similarities between MIG and TIG welding.
- Arc Welding – Both MIG and TIG are arc welding as an electric arc forms between the electrode and the workpiece.
- Bare Electrode – Both the processes use a bare electrode. This means there is no application of flux-coated electrodes. Hence, there is no spatter formation and less after-process cleaning.
- Shielding Gas – Both processes use a shielding gas to protect the welded part from reacting with elements in the air.
- Conductive Metals – You can weld only conductive metals using MIG and TIG welding. This is because the base metal has to conduct the arc to heat it up and melt.
Differences between MIG and TIG welding
| Parameters | MIG Welding | TIG Welding |
| Equipment Used | Welding gun, welding power supply, consumable wire electrode, and active shielding gas. | Welding torch, constant-current power supply, non-consumable electrode, and inert shielding gas. |
| Electrode Type | Uses a consumable electrode that is continuously fed during the process. | Uses a non-consumable electrode that stays intact throughout the process. |
| Electrode Material | Material selection depends on the base material | Tungsten |
| Power Supply | Uses constant voltage direct power supply | Uses constant-current welding power supply |
| Shielding Gas | A mixture of active and inert gas. | An inert gas, specifically Argon. |
| Polarity | Uses Direct Current Electrode Positive(DCEP) Polarity for faster deposition rate. | Uses Direct Current Electrode Negative(DCEN) Polarity for the greater lifespan of the electrode. |
| Filler Material Requirement | No additional filler material required as the electrode already has it. | May need to supply filler material external, if needed. |
| Wire Feeding | Need continuous wire feeding. | No need of wire feeding. |
| Speed | Fast | Slow |
| Working Position | Works in a certain position only. | Can work in any position. |
| Filler Deposition Rate | High | Low |
| Spatter | Some spatter produced. | No spatter produced. |
| Skill Requirement | Basic skills and experience are enough. | Requires highly skilled welders with some experience. |
| Weld Bead Appearance | Not so good and uniform. | Neat and clean appearance. |
| Suitability | Suitable for homogeneous welding. | Suitable for autogenous welding though can be used for homo and heterogeneous welding. |
Typical Materials Used in MIG and TIG Welding
MIG welding is suitable for thick materials, while TIG welding is preferred for thin materials. Ideally speaking, both processes are suitable for a wide range of materials. From a technical perspective, TIG welding is best for aluminum and magnesium, and MIG welding is the best for steel and alloys.
Generally speaking, typical weld materials in MIG welding are carbon steel, stainless steel, copper, nickel, bronze, brass, and alloys of different metals.
Typical weld materials in TIG welding are aluminum, magnesium, titanium, low-alloy steel, mild steel, and alloys of aluminum and magnesium.
Conclusion
MIG and TIG welding processes are extremely popular for industrial applications. Both have their distinct benefits and applications, which we have explained in detail. Hope the article has helped you to understand all the different aspects of MIG and TIG welding. You must now have a clear perception about which process is perfect for your welding requirement.