It is understandable if the CPU in your PC is maxing out when you are playing games or running high-demand applications (such as video editing for instance). What’s unusual is if the CPU usage is high even when you are not doing anything (or only running simple tasks). There will always be some processes running in the background that are not necessarily initiated by you (but are essential for normal functioning of PC). But if you notice the CPU running high and fans blowing air all the time, then this might be an indication of an underlying problem. So, how to lower CPU usage and bring things back to normal?
Fortunately, there are some easy fixes for this issue and lower CPU usage on a Windows computer. In fact, we are here with a complete beginner’s guide and detailed instructions on how to lower CPU usage in Windows. In the process, we will understand how to check the current CPU usage in a Windows machine and some of the common reasons for high CPU usage.
Outline
Toggle- Introduction
- How to Check the Current CPU Usage?
- Why is My CPU Usage So High?
- How to Lower CPU Usage?
- 1. Reboot Your Computer
- 2. End/Restart Background Processes
- 3. Update all Device Drivers
- 4. Scan your Computer for Malware, Viruses
- 5. Check Power Options in Windows
- 6. Close Unnecessary Applications
- 7. Turn Windows Notifications Off
- 8. Disable Windows Delivery Optimization
- 9. Disable Any Animations or Effects
- 10. Clean Your PC
- 11. Perform a System Restore
- 12. Add More RAM
- 13. Disable Unneeded Startup Programs
- 14. Reinstall Windows on your Computer
- 15. Overclocking the CPU
- 16. Install a New CPU
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Introduction
The CPU or Processor is the most important component in your PC. This is due to the fact that each and every program, application, game, and task running on your computer is handled by the CPU. On the hardware side, all the other components of the PC such as RAM, Graphics Card, SSD, etc. respond to the instructions from the CPU. Hence, having a reliable and functioning CPU at all times is very important.
We expect applications to launch instantly as soon as we click them. This is where the speed and power of the CPU comes into play. A CPU that is fast and powerful can handle multiple complex tasks without an issue. But what if there are a few background processors that hog up the processor (using up all the resources) and cause high CPU usage?
It will surely impact the performance of your computer. You might notice jerks in mouse cursor movement, applications/programs become laggy (or even crash), and the temperature of the CPU will rise significantly (which causes the fans to run high all the time making loud noise). This is why keeping an eye on the CPU usage is a good habit.
How to Check the Current CPU Usage?
So, the next obvious question is how to check or monitor CPU usage, especially in a Windows system? There are a couple of easy and straightforward ways as well as some slightly not so simple ways to check the CPU usage.
Task Manager
Probably the simplest and most straightforward way to check CPU usage is through Windows’ Task Manager. It is a very powerful system monitoring tool and the best thing is it is included with Windows. Now there are multiple ways to launch the Task Manager. Let us see them all.
- Keyboard Shortcut Ctrl+Shift+Esc: This shortcut directly opens Task Manager without needing to go through an intermediate screen.
- Right-click on Windows Taskbar: Right-clicking on an empty area of the taskbar brings up a menu where you can select “Task Manager”.
- Windows Search in Start Menu: You can type “task manager” in the Windows Start Menu search box and select Task Manager from the results.
- Win+R and taskmgr.exe: Opens the Run dialog (Win+R), where you can type taskmgr.exe and press Enter.
- Ctrl+Alt+Delete and Task Manager: Pressing Ctrl+Alt+Delete brings up a screen where you can select Task Manager from the options.
- File Explorer address bar: You can type taskmgr in the address bar of File Explorer and press Enter to launch Task Manager.
- Command Prompt or PowerShell: Typing taskmgr in either Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell and pressing Enter will open Task Manager.
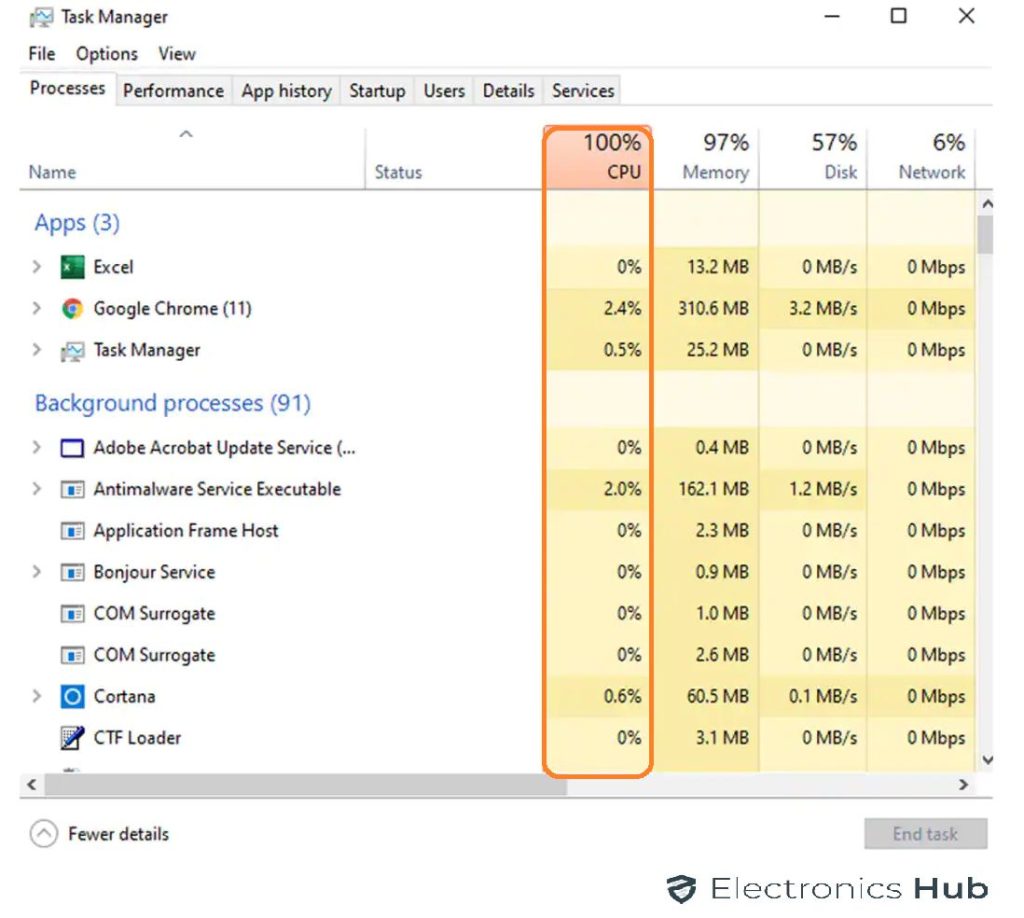
Once you launch the Task Manager, click on the More details option in the Task Manager window to open its expanded view. Now, head over to the Performance tab where you can check various details regarding your computer’s hardware including its CPU.
In order to check the current CPU usage, you need to go to the CPU tab where you can see each and every detail of your computer’s CPU usage.
Command Prompt
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type cmd and press Enter to open Command Prompt.
- Type wmic cpu get loadpercentage and press Enter.
- This command will display the current CPU usage as a percentage.
PowerShell
- Press Windows + X to open the Power User menu.
- Select “Windows PowerShell” from the menu that appears.
- In the PowerShell window, type the following command and press Enter
- Get-Counter -Counter “\Processor(_Total)% Processor Time” -SampleInterval 1 -MaxSamples 5
- This command will show the current CPU usage as a percentage over a short sampling period (5 samples at 1-second intervals).
Third-party Software
There are several third-party tools that help you monitor CPU usage (among other things). One such tool (and one of our favorites) is the HWMonitor from CPUID (who also make the CPU-Z tool).
Why is My CPU Usage So High?
There is only CPU in a PC but hundreds of processes and applications that need to run. So, the operating system does an interesting and important job of scheduling the CPU time to different processes based on scheduling algorithms (priority, time-sharing, etc.).
When one or two processes take-up a significant amount of CPU time, it leads to high CPU usage and slowdown or lagging of other applications (as they couldn’t proper attention from CPU). Hence, very high CPU usage usually means the resources allocated to other processes becomes very limited.
Once you start the Task Manager (or any other ways to monitor CPU parameters) and notice the CPU running 100% all the time, the obvious question is “Why is my CPU usage so high?”.
Background Processes
One of the main reasons why the CPU usage is high is background processes. These processes are essential for a smooth operation of the system (antimalware service, Networking, System Interrupts, etc.).
Sometimes when you close an application, there will still be associated processes that keep running in the background (we are looking at you Chrome). If such background processes start to accumulate in large numbers, there is chance that they utilize a good number of resources making them inaccessible for other applications. This in turn increases the CPU usage as the applications are always fighting for proper CPU time. These background processes might also include Windows processes.
Resource-Intensive Applications
Applications such as video editing and rendering, 3D Modelling or CAD, Code Compilations, and Games are extremely CPU intensive. If the CPU in your PC isn’t capable of handling such applications, then you will notice 100% CPU usage for the most part.
WMI Provider Host
The WMI Provider Host (WmiPrvSE.exe) is a Windows system process that is part of the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) infrastructure. WMI is a powerful framework provided by Microsoft in Windows operating systems that allows administrators and developers to access and manipulate management information in an enterprise environment.
WMI Providers are software components that expose management data about a particular aspect of the system or application. They provide access to configuration settings, status information, performance data, and more.
The WMI Provider Host is the process that hosts these WMI providers. Each provider runs within its own instance of the WMI Provider Host process (WmiPrvSE.exe).
Normally, the WMI Provider Host process should not consume excessive CPU or memory resources. High CPU usage by this process can sometimes indicate issues with specific WMI providers or queries.
Faulty Drivers
All the hardware components of a PC need appropriate drivers to communicate with the operating system (and thereby the CPU). If a particular driver is corrupt or out-of-date, then it might put a toll on CPU performance.
Outdated Software
Similar to drivers, outdated software or applications can also increase the CPU usage. This is applicable to the Windows operating system as well as individual applications.
Viruses or Malware
This one is obvious. Viruses or malicious software, if undetected, appear like regular applications but run in the background taking up precious CPU time. This will definitely increase the CPU usage.
Improper Hardware Configuration
Sometimes, changes to hardware settings such as BIOS or graphics can increase the CPU usage. These settings can be as simple as changing the memory profile in BIOS or forcing applications to use dedicated graphic card (even when not necessary).
Too Many Programs
Running too many applications simultaneously can dramatically increase the CPU usage. The situation becomes worse if you are running multiple resource hungry applications at the same time.
Dirty Fans (And Overheating CPU)
Heat is an enemy of processors. The main job of the heatsink and the fans on a CPU is to keep it cool. But over years, these fans accumulate dust and couldn’t move as much air as expected. As a result, the CPU temperature rises, which in turn leads to thermal throttling.
Since the CPU isn’t running at its full potential, applications might become laggy and the overall CPU usage increases.
How to Lower CPU Usage?
If the CPU usage of your PC is high (90 – 100%) all the time, then you have to identify and diagnose the issue before it causes a major damage to the CPU or any other hardware. So, how to lower CPU usage? Let us now see some fixes for this problem.
1. Reboot Your Computer
The first solution is the good old trick of rebooting or restarting your PC. Before taking any drastic measures to fix high CPU usage, try to properly shutdown your PC and restart it. This process will clear the cache, remove temporary files, applies updates or patches to drivers or applications, and stops unnecessary background processes.
You can reboot your computer directly from the Start Menu similar to how you would do it normally. If the source of high CPU usage is as simple as cache or temporary files, then a simple system reboot will fix it for you. This action will terminate any background processes that are hogging up the processor and the CPU usage will be lowered quite a lot. But if you are noticing high CPU usage even after restarting your PC, then the issue might need further analysis.
2. End/Restart Background Processes
While rebooting your computer should get rid of most background processes, some of them might be still running. And in that case, the CPU usage of your computer might not be lowered that much. Not all background processes are evil but the ones that require a good portion of CPU time definitely are. Is there a way to deal with such unnecessary background programs? Fortunately, Windows allows you to manually end as well as restart background processes quite easily.
The Task Manager comes with a powerful feature that lists out all the applications, processes, tasks, and services that are running at any time. If you feel that a particular process or application is the reason for high CPU usage, then you can either restart that task or terminate the task entirely.
This can be quite great for completely getting rid of a certain background process, as well as for restarting any important background processes which you think are not performing like they should. In such a case, you can end or restart processes from the Task Manager in Windows as given here:
- As shown earlier, press control + shift + escape on your keyboard to open the Task Manager.
- Once inside the Task Manager window, open the Processes tab where you can see all of the currently running processes on your computer.
- Now, click on the CPU usage indicator which will sort all of these processes as per CPU usage where any processes which are having high CPU usage will come on the top.
- You can then click on End task on this process to terminate it which should lower the CPU usage quite a lot.
- If you feel like a given process is highly important, then make sure to click on Restart so that it will launch again.
3. Update all Device Drivers
Even if you are not using any external peripherals along with your laptop or desktop, there are still going to be a large number of hardware devices connected to it including internal components.
For all of these hardware devices, Windows has a dedicated device driver installed which is there for offering communication between your computer and the hardware device. Although, this also means that if a given device driver is not working properly, then its corresponding hardware device may not work properly. This can even cause high CPU usage in some cases because of which you should update all device drivers in Windows by using Device Manager as explained here:
- For opening Device Manager in Windows, you have to first press Windows Key + X keyboard on your computer and select Device Manager from the list.
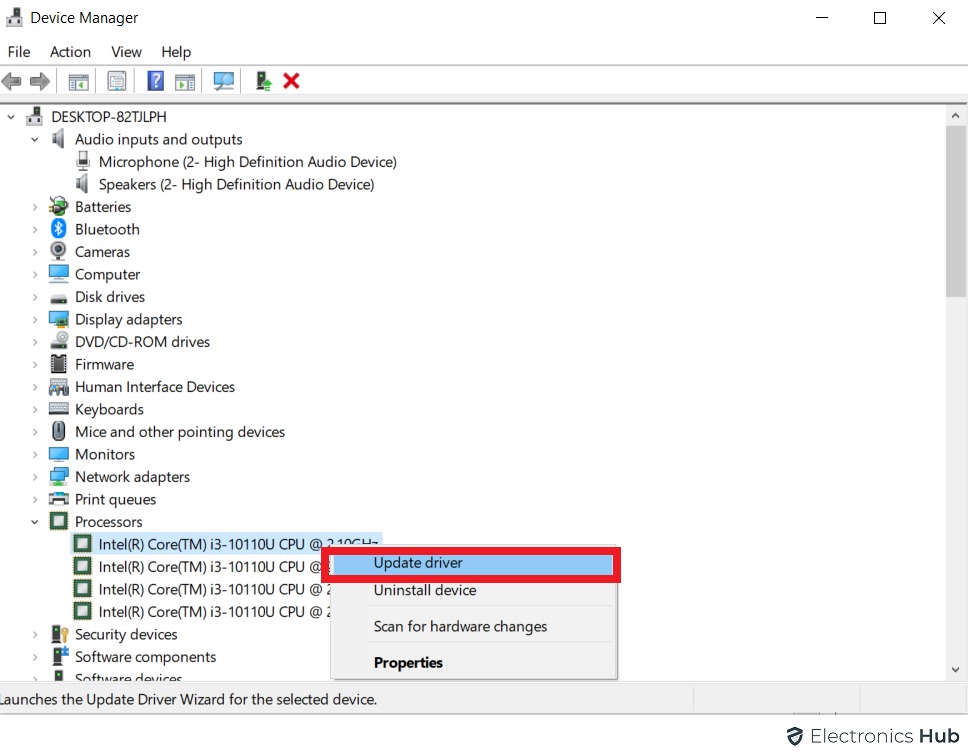
- You can then expand each and every menu in Device Manager to get a complete list of all the various hardware devices installed in it.
- And in order to update all device drivers, you have to right click on all of these devices one by one after which you can select the Update driver for a given device.
- Finally, click on the Search automatically for updated drivers in the newly opened window to update all device drivers to the latest version on your computer.
4. Scan your Computer for Malware, Viruses
If your computer is having CPU usage, then there is quite a bit of a chance that it is being caused due to possible malware or any other type of file infection on your computer. Such malware and other infected files run in the background of your computer and use your CPU for all kinds of operations and usage.
Hence, in case of high CPU usage, scanning your computer for potential malware infection is highly important if you want to lower CPU usage. You can use the Windows Defender to do a full scan of your computer which will scan all files and programs for any potential malware or infected files which will be automatically removed for potentially lowering your computer’s CPU usage.
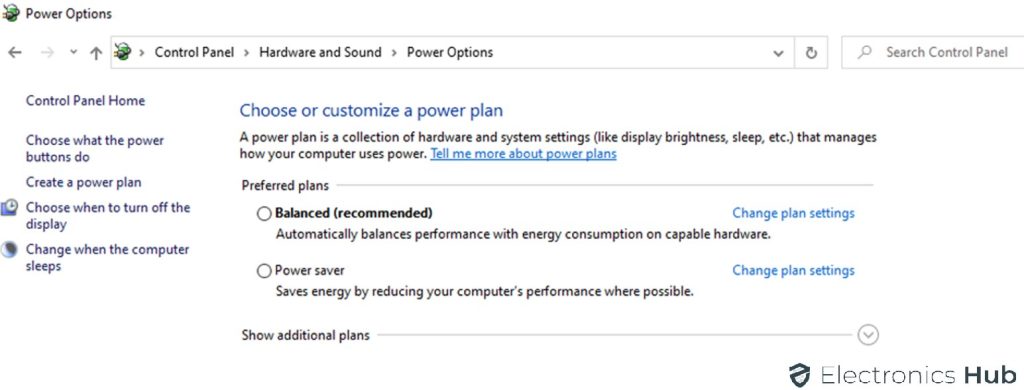
5. Check Power Options in Windows
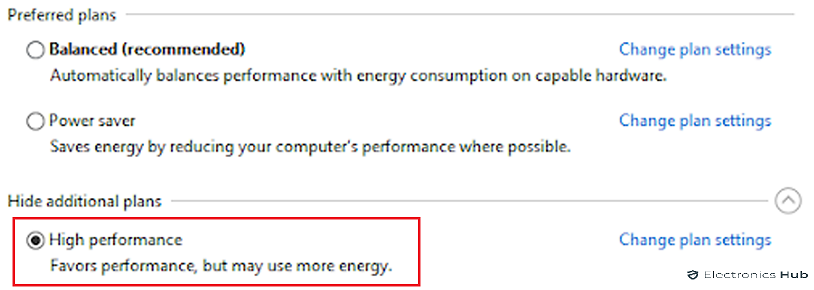
In case that you are using a laptop and not a desktop, then it is going to have multiple power options. Most modern laptops will have 3 such power options or power plans. This includes a battery saver plan, a balanced plan, and a high-performance mode for getting the most out of your computer.
Talking about the battery saver plan, it works by lowering the power of your CPU and other internal components for reducing power consumption and potentially increasing your laptop’s battery life. While this does increase the battery life, reduced CPU power also means that the same task will use your CPU more as it would have used it in a high-performance power plan. Hence, make sure that you are either using the balanced plan or the high-performance power plan to lower CPU usage on your laptop.
6. Close Unnecessary Applications
If you have too many applications running simultaneously, then close some of them that you feel are unnecessary. This will free-up a lot of resources and mainly will reduce the CPU usage. You can once again take the help of Task Manager to list out the apps. From the list, pick the task that is no longer needed, right-click on it, and select the ‘End task’ option.
7. Turn Windows Notifications Off
Windows notifications themselves don’t typically consume a significant amount of CPU resources, but they can be associated with background processes or services that might use CPU cycles. Disabling notifications reduces the overall background activity, which can contribute to slightly better performance and responsiveness.
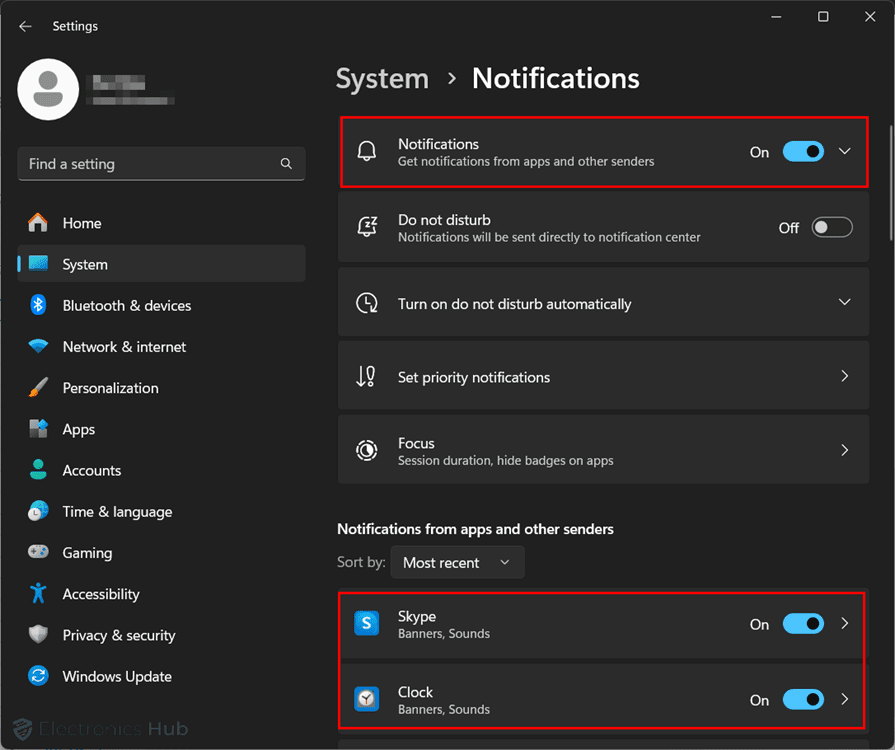
In Windows 11, you can manage and turn off notifications through the Settings app. Here are the steps to do so:
- Open the Settings app by clicking on the Start menu (Windows icon) and selecting the gear icon (Settings). If you cannot find the shortcut, then start searching for settings or use the keyboard shortcut Win+I. In the Settings window, click on “System” from the list of options.
- In the System settings, click on “Notifications”. This section allows you to manage notifications for various apps and system features.
- You can turn off all the notifications by toggling the main Notifications option on the top. Alternatively, you can customize notification settings for a specific app from the list below.
8. Disable Windows Delivery Optimization
Windows Delivery Optimization is a feature in Windows 10 and Windows 11 that helps to reduce bandwidth usage and speed up software updates and app downloads. It works by allowing your computer to download updates and apps from other computers on your local network or from the internet.
Delivery Optimization might use some CPU resources and network bandwidth while downloading updates or apps in the background. This could potentially impact the overall performance of your system if you are performing CPU-intensive tasks simultaneously. If your computer shares updates with others on the network or internet, it may intermittently use CPU resources to manage and transfer data.
- To turn this off, open Settings app first using the keyboard shortcut ‘Windows + I’. Select ‘Windows Update’ from the left-hand sidebar and then click on ‘Advanced options’.
- In the ‘Additional options’ section, click on ‘Delivery Optimization’. Then toggle the ‘Allow downloads from other PCs’ off.
9. Disable Any Animations or Effects
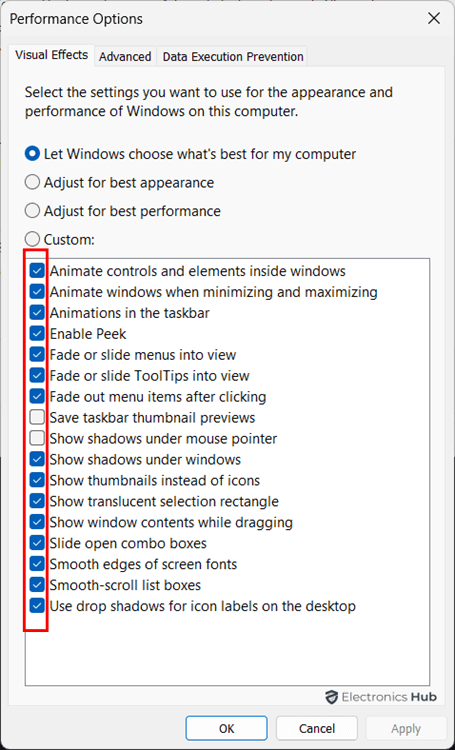
Visual Effects settings in Windows control various graphical enhancements and animations that improve the user interface’s aesthetics and usability. Visual effects such as animations, transparency, and shadow effects can consume CPU and GPU resources. Disabling them reduces the workload on these components, potentially improving overall system responsiveness.
- Open Settings app (using Windows + I keyboard shortcut). Select ‘System’ tab from the left-hand sidebar and scroll down to select ‘About’.
- Under the ‘Device Specifications’, click on the ‘Advanced system settings’ option. This will pop-up a new window. Click on ‘Settings’ under the Performance option. You will have a list of settings you can customize to reduce CPU usage due to animations and other visual effects.
10. Clean Your PC
If the fans and filters of your PC are dirty, give them a proper cleaning. If the thermal paste is too old, clean the existing thermal paste and apply fresh thermal paste so that heat conduction will be better.
11. Perform a System Restore
System Restore is a feature in Microsoft Windows that allows users to revert their computer’s state (system files, installed applications, Windows Registry, and system settings) to a previous point in time, called a “restore point.” This can be useful if the system becomes unstable or if recent changes (like software installations or updates) cause problems. Here are the steps to perform System Restore in Windows:
- Press the Windows Key + R to open the Run dialog box, type rstrui and press Enter. This will open the System Restore window.
- In the System Restore window, click on “Next” to see a list of available restore points.
- Windows automatically creates System Restore points before significant system events like software installations, Windows updates, or critical changes.
- Choose a restore point from the list that you believe corresponds to a time when your system was working correctly and click on “Next”. Windows will then restart and begin the System Restore process. After the restart, log in to your system and check if the issues you were experiencing such as high CPU usage have been resolved.
12. Add More RAM
Adding more RAM to a PC can indirectly reduce CPU usage in certain situations because of how modern operating systems manage memory and applications. When a computer runs low on RAM, the operating system compensates by using a portion of the hard drive (called the page file or swap space) as virtual memory. This process is known as paging or swapping.
If RAM is insufficient, the CPU has to move data between RAM and the page file frequently, which can significantly slow down performance. This constant swapping requires CPU resources, increasing CPU usage.
With more RAM available, the operating system can keep more applications and data in RAM instead of swapping them out to the slower hard drive. This allows applications to run more smoothly and reduces the need for the CPU to manage memory swapping tasks.
Applications that require a lot of memory, such as video editing software, virtual machines, or large databases, benefit directly from more RAM. When these applications have enough RAM, they can perform operations faster and more efficiently, reducing the overall workload on the CPU.
13. Disable Unneeded Startup Programs
Startup programs in Windows are applications or services that automatically launch when your computer boots up. These programs are typically configured to start with Windows for convenience, allowing certain applications to be ready for use immediately after the system starts.
When Windows boots up, it allocates CPU resources to initialize all startup programs. If there are many startup programs, they can collectively consume CPU cycles during the boot process. Disabling unnecessary startup programs means fewer applications are competing for CPU resources during startup, potentially speeding up the boot process and reducing CPU usage at that critical time.
- Right-click on the taskbar and select “Task Manager” from the menu that appears, or press Ctrl + Shift + Esc.
- In Task Manager, click on the “Startup apps” tab. This will show you a list of all programs that launch when Windows starts.
- Right-click on any program you want to disable and select “Disable”.
Changes to startup programs usually take effect after you restart your computer. Once the system restarts, your system should benefit from reduced CPU usage and improved performance, especially if you disabled several unnecessary startup programs.
14. Reinstall Windows on your Computer
As a last resort, you can also consider reinstalling Windows on your computer if you are facing high CPU usage quite often. This can be quite handy if any of the programs that you have installed is causing the same. Apart from getting rid of high CPU usage programs, reinstalling Windows will also reset all Windows settings which might be increasing the CPU usage in the first place. Hence, you can try reinstalling Windows on your computer using the Microsoft Media Creation Tool and then check your CPU usage which should be lowered quite a lot.
15. Overclocking the CPU
Overclocking a CPU refers to the process of increasing the clock rate of a computer’s central processing unit (CPU) beyond the manufacturer’s specifications. It can potentially reduce CPU usage in certain scenarios because it allows the CPU to process instructions faster than at its stock settings.
This means tasks that would normally take longer to execute can be completed more quickly. As a result, the CPU may not need to operate at maximum usage for as long, potentially reducing overall CPU usage in some contexts.
However, overclocking a CPU can increase power consumption and heat production, potentially reducing the lifespan of the CPU. It can also cause immediate damage if temperatures exceed safe limits.
16. Install a New CPU
If you tried all these steps and still couldn’t lower the CPU usage, then maybe it is time to upgrade to a new CPU. A newer, more powerful CPU can handle tasks more efficiently. This means it can complete tasks faster or handle more demanding tasks without maxing out its capacity. In such cases, the CPU may run at a lower percentage of its maximum capacity compared to an older, less powerful CPU doing the same tasks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a normal CPU usage percentage?
Answer: Normal CPU usage varies, but typically, idle usage hovers around 10-30%. Under load, it can spike higher, even up to 70-80% for intensive tasks like gaming or rendering.
Can background sync services affect CPU usage?
Answer: Yes, background sync services, especially those syncing large amounts of data or running frequent updates, can significantly impact CPU usage by consuming processing power during synchronization operations.
What are the best tools to monitor CPU usage?
Answer: Popular tools include Task Manager (Windows), Activity Monitor (Mac), and htop (Linux). For Windows, there are several third-party tools like Process Explorer and HWMonitor.
What settings can I adjust to lower CPU usage?
Answer: You can lower CPU usage by adjusting power settings (e.g., power plans on Windows), disabling unnecessary startup programs, optimizing background services, and reducing visual effects.
Can browser extensions affect CPU usage?
Answer: Yes, browser extensions can increase CPU usage, especially if poorly coded or running resource-intensive tasks like ad-blocking or real-time content scanning. Disable or remove extensions to reduce CPU load in browsers.
Conclusion
Those of you who have an old CPU or an entry level one might be worried about the CPU usage quite often due to the limited total performance offered by it. And even if you have a high end and a powerful processor, you would still want it to be used by only the programs that you are using. In other words, to ensure that the processor for your computer is functioning at optimum performance, you would want to lower its CPU usage as much as possible.
For the same, we have already given detailed instructions and a complete tutorial on how to lower CPU usage on your computer. You can also learn more about checking the current CPU usage in Windows to ensure that your processor is not being overused by background tasks and processes. If you have gone through all the information regarding how to lower CPU usage in Windows computers, make sure to share your thoughts in the comments section. You can also post any questions down there if you have any!