Modern motherboards come with a plethora of features that may not be apparent to the average buyer but can significantly impact the system’s performance. One such critical feature is the PCIe slots. If you are building a computer, whether it is for basic applications or gaming, you should check out this feature carefully as it affects the performance of other accessories as well as the upgradeability of the system.
Therefore, we are going to talk about this feature in depth in our guide today. We will also talk about different versions of these slots and their importance in terms of application and performance.
Outline
ToggleWhat is PCI Express?
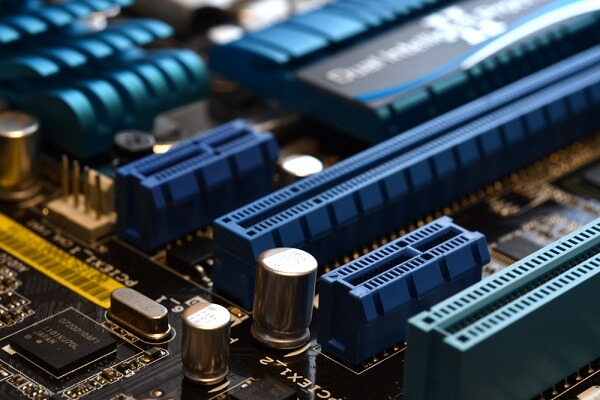
The most common PCIe configurations include x1, x4, x8, and x16 lanes. Each lane represents a dedicated data pathway that can be used for communication between the motherboard and the connected device, such as a graphics card, storage device, or network adapter. The higher the number of lanes, the greater the bandwidth available for data transfer, which directly impacts the performance of the connected component.
In addition to increased data transfer speeds, PCIe also introduced several other features that enhance its efficiency and functionality. These include the ability to negotiate link speeds dynamically, enabling devices to operate at their maximum supported speeds. PCIe also allows devices to enter low-power states when not in use, contributing to overall energy efficiency.
What Do You Mean By The PCIe x16?
The PCIe x16 refers to the specific configuration of the PCIe slot on a motherboard. The “x16” part refers to the number of data lanes available for communication between the motherboard and the connected device, which, in this case, is 16 lanes. Thus, A PCIe x16 slot provides 16 lanes for data transfer, making it the slot with the highest available bandwidth among the commonly used PCIe configurations. It is primarily used for connecting graphics cards, which often require high data transfer rates to handle graphics-intensive tasks like gaming, video rendering, and 3D modeling.
The higher number of lanes available in a PCIe x16 slot allows for significantly higher data transfer rates compared to other configurations, such as x1, x4, or x8 slots. This increased bandwidth is crucial for graphics cards, as it ensures that the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) can communicate with the CPU and system memory efficiently, delivering smooth and high-quality visuals.
Applications of PCIe x16 Slots
PCIe x16 slots find various applications due to their high bandwidth and data transfer capabilities. Some of the primary applications of PCIe x16 slots include:
- Graphics Cards: The most common and well-known application of PCIe x16 slots is for connecting graphics cards (GPUs) to the motherboard. Graphics cards require significant data bandwidth to process and render complex 3D graphics, video, and other visual elements in applications like video games, video editing, 3D modeling, and animation. PCIe x16 slots provide the necessary high-speed data transfer to ensure smooth and immersive visuals, making them essential for gaming enthusiasts, content creators, and professionals in the visual design industry.
- Heavy Duty Networking Cards: PCIe x16 slots are also utilized for connecting high-performance networking cards. In data centers, servers, and workstations that require intensive networking capabilities, specialized networking cards can be installed in PCIe x16 slots to handle heavy data loads. These cards often offer advanced features like multiple Ethernet ports, high throughput, and low-latency communication, making them ideal for data-intensive tasks such as large-scale data transfers, cloud computing, and data analysis.
- Heavy Duty Storage Cars: PCIe x16 slots can be used to accommodate high-speed storage devices, particularly NVMe SSDs. NVMe SSDs offer significantly faster data transfer rates compared to traditional SATA-based SSDs, making them ideal for applications where storage speed is critical, such as content creation, video editing, and database management. By using a PCIe x16 slot, these storage devices can access the maximum available bandwidth, ensuring speedy access to data and reduced loading times.
- Specialized Accelerator Cards: PCIe x16 slots are increasingly used for various specialized accelerator cards that offload specific tasks from the CPU to improve overall system performance. Examples include FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) cards for hardware acceleration, AI (Artificial Intelligence) accelerators for machine learning tasks, and HPC cards for scientific simulations and computations. These cards leverage the high bandwidth provided by PCIe x16 slots to deliver significant performance improvements in their respective applications.
Versions of PCIe x16 Slot
The PCIe x16 slot version is a crucial factor that determines the data transfer speed and capabilities of the slot. Each PCIe version represents an evolution of the standard, offering increased bandwidth and improved features. The version of the PCIe x16 slot directly impacts the performance of connected devices, especially graphics cards, as it determines how much data can be transferred between the device and the motherboard per second.
1. Version 1.0
Introduced in 2003, PCIe 1.0 was the first version of the standard. It offered a data transfer rate of 2.5 GT/s per lane in each direction. A PCIe x16 slot in version 1.0 provided a total bandwidth of up to 40 Gbps in each direction.
2. Version 2.0
Released in 2007, PCIe 2.0 doubled the data transfer rate to 5 GT/s per lane in each direction. A PCIe x16 slot in version 2.0 provided a total bandwidth of 80 Gbps. PCIe 2.0 was also backward compatible with PCIe 1.0, meaning PCIe 2.0 devices could be used in PCIe 1.0 slots, but at the lower speed of 2.5 GT/s per lane.
3. Version 3.0
PCIe 3.0 further doubled the data transfer rate to 8 GT/s per lane in each direction in 2010. A PCIe x16 slot in version 3.0 offered a total bandwidth of 128 Gbps in each direction, approximately 16 GB/s of total data transfer. PCIe 3.0 remained backward compatible with PCIe 2.0 and PCIe 1.0 devices.
4. Version 4.0
In 2017, PCIe 4.0 was released. PCIe v4 yet again doubled the data transfer rate again to 16 GT/s per lane in each direction. Thus, a PCIe x16 slot in version 4.0 provided a total bandwidth of 256 Gbps in each direction, offering nearly 32 GB/s of total data transfer.
5. Version 5.0
Released in 2019, PCIe 5.0 continued the trend by offering a data transfer rate of 32 GT/s per lane in each direction. A PCIe x16 slot in version 5.0 offers a total bandwidth of 512 Gbps in each direction, approximately 64 GB/s of total data transfer.
6. Version 6.0
The latest version, PCIe 6.0, was announced in 2021 and sure enough, offers another doubling of the data transfer rate to 64 GT/s per lane in each direction. A PCIe x16 slot in version 6.0 offers a total bandwidth of 1,024 Gbps in each direction. So, approximately 128 GB/s of total data transfer is possible with version 6.
| PCIe Generation | x1 | x2 | x4 | x8 | x16 |
| 1 | 0.25 GBps | 0.5 GBps | 1 GBps | 2 GBps | 4 GBps |
| 2 | 0.5 GBps | 1 GBps | 2 GBps | 4 GBps | 8 GBps |
| 3 | 0.9 GBps | 1.9 GBps | 3.9 GBps | 7.8 GBps | 15.7 GBps |
| 4 | 1.9 GBps | 3.9 GBps | 7.8 GBps | 15.7 GBps | 31.5 GBps |
| 5 | 3.9 GBps | 7.8 GBps | 15.7 GBps | 31.5 GBps | 63 GBps |
PCIe x16 – FAQs
Ans: Whether you need a PCIe x16 slot depends on your specific requirements. For example, If you are building a gaming PC or working with graphics-intensive applications such as video editing, 3D modeling, or CAD software, a PCIe x16 slot is essential. Also, if you are planning to use multiple graphics cards in a multi-GPU setup, a PCIe x16 slot is required for each GPU.
Ans: The main difference between PCIe and PCIe x16 lies in their physical configurations and the number of data lanes they support. PCIe is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard that allows various hardware components to communicate with the motherboard. On the other hand, PCIe x16 means a specific configuration of the PCIe slot with 16 data lanes.
Ans: The “x16” in PCIe x16 stands for the number of data lanes available in the slot. It represents the physical configuration of the slot and indicates how many separate data pathways are available for communication between the motherboard and the connected device.
In the case of PCIe x16, there are 16 data lanes in the slot. Each data lane is capable of bidirectional data transfer, meaning data can flow in both directions simultaneously. These lanes act as individual pathways through which data travels to and from the connected device, such as a graphics card.
Ans: Whether a PCIe x16 slot can operate at its full speed depends on several factors such as the version of the PCIe standard supported by the slot, the specific hardware components connected to the slot, and any potential limitations imposed by the motherboard. If both the motherboard and the device support the same PCIe version (e.g., PCIe 5.0), the slot can operate at the full speed designated by that version.
In certain cases, the motherboard’s BIOS may have settings that affect the PCIe slot speed. For example, some motherboards allow users to manually set the PCIe mode to a specific version.
Conclusion
PCIe is a standard connectivity port on the motherboard that connects hardware components to the motherboard, with the PCIe x16 slot being particularly important for graphics cards and high-bandwidth devices. The PCIe version determines data transfer speed, with newer versions offering increased performance. In this guide, you can also find comparisons of different PCIe versions from 1.0 to 6.0 along with their respective data transfer rates. However, whether you need a PCIe x16 slot depends on usage, such as gaming and graphics-intensive tasks. If the motherboard and connected device support the same PCIe version and use all 16 lanes, the PCIe x16 slot will be able to operate at its full speed, offering numerous benefits with all connected devices.

