Is your computer running sluggishly? Are programs taking ages to load? Are you tired of waiting for files to transfer? If so, your hard drive might be the culprit.
Maintaining a healthy hard drive is vital for optimal computer performance. A slow hard drive can result in lagging programs, sluggish loading times, and an overall frustrating user experience. Fortunately, there are several ways to test your hard drive speed and identify potential issues.
In this article, we present a comprehensive guide on testing your hard drive speed in Windows. We’ll walk you through various methods, including utilizing built-in tools, third-party software, and even command prompts. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge and tools necessary to diagnose any problems and optimize your hard drive for peak performance.
Outline
Toggle- What is the Purpose of a Hard Drive Speed Test?
- Key Components Measured in a Hard Drive Speed Test Include:
- Things you Have to Know Before You Start a Hard Drive Test
- How to Test Hard Drive Speed on Windows 10/11
- Unleashing Your Hard Drive’s Potential: Optimization Tips
- Test Hard Drive Speed Windows – FAQS
- Conclusion
What is the Purpose of a Hard Drive Speed Test?
A Hard Drive Speed Test, also referred to as a disk speed test or disk benchmark, serves as a diagnostic tool specifically designed to assess and evaluate the performance of a computer’s storage devices, predominantly hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs), in terms of their read and write data speed. This speed is typically measured in megabytes per second (MB/s). Faster read speeds enable quicker access to files and programs, while faster write speeds facilitate more efficient data saving and file transfer.
Also Check:
Key Components Measured in a Hard Drive Speed Test Include:
- Sequential Read and Write Speeds: This metric quantifies the rate at which a storage device can sequentially read or write substantial data blocks. It plays a vital role in tasks like loading sizable files or streaming media, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
- Random Read and Write Speeds: This evaluation measures the device’s capacity to efficiently handle small data requests that are randomly distributed. The speed of random access is crucial for tasks that involve a multitude of small files or applications.
- Access Times: The term “access time” pertains to the duration required for a storage device to locate and retrieve data. Decreased access times play a vital role in enhancing the overall system responsiveness, leading to a swifter and more efficient user experience.
- IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second): IOPS, or Input/Output Operations Per Second, is a metric that quantifies the storage device’s capability to perform both read and write operations within a single second. This parameter holds significant significance for tasks that entail a multitude of small, random data accesses, like gaming or database operations.
- Latency: Latency refers to the time elapsed between requesting and retrieving data. A lower latency value signifies a storage device that is more responsive and swift in its operations.
Things you Have to Know Before You Start a Hard Drive Test
Before initiating your hard drive speed test, there are important steps you can take to greatly enhance the accuracy and reliability of your results. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
1. Close Unnecessary Programs
Running multiple programs in the background can significantly impact your test results. Ensure you close all unnecessary applications, including background processes, to optimize your system’s performance and provide the hard drive with uninterrupted access for accurate read and write speed measurements.
2. Plug in for Stable Power
Testing your hard drive requires a consistent and stable power supply. To avoid interruptions and inaccurate results, connect your laptop or computer to a reliable power source. Fluctuating power can negatively impact performance and lead to misleading measurements.
3. Choose the Right Tool for the Job
Various methods and tools are available for testing hard drive speed, each offering different levels of detail and complexity. Consider your technical expertise and desired level of information when selecting your testing tool. There are Built-in tools in your system or Third party tools. Select one of them.
4. Consider Additional Factors
- Background Processes: While closing unnecessary programs is crucial, some essential background services might still be running. Consider using a tool like “Process Hacker” to identify and temporarily disable unnecessary background processes for a more accurate test.
- File Fragmentation: Fragmented files can impact your hard drive’s performance. Consider defragmenting your hard drive before testing to ensure optimal results.
- Cooling: Hard drives can heat up during operation, potentially affecting performance. Ensure proper ventilation around your computer to avoid thermal throttling and inaccurate results.
How to Test Hard Drive Speed on Windows 10/11
Now that you’ve prepared your hard drive for testing and equipped yourself with the right tools, it’s time to delve into the different methods for uncovering its true speed potential. Let’s explore how to test your hard drive speed on Windows 10/11:
How to Test Hard Drive Speed Using Command Prompt
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
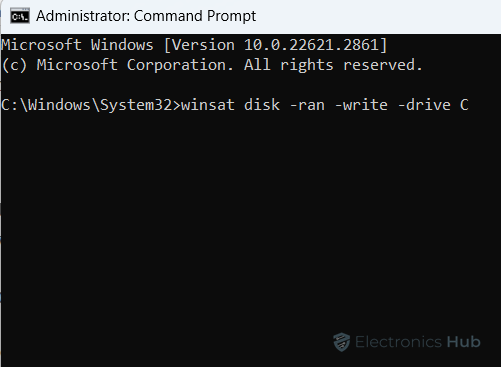
- Type the following command and press Enter: winsat disk -ran -write -drive (drive letter)
- Replace “(drive letter)” with the actual letter assigned to your hard drive (e.g., C, D, E). winsat disk -ran -write -drive C
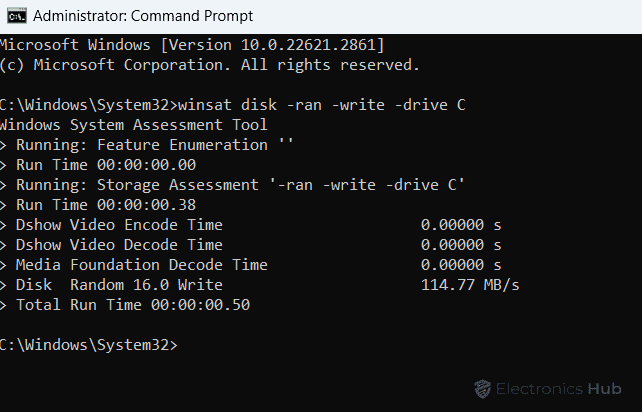
- Wait for the command to finish. then, Scroll up the command prompt window to view the results.
- Now you will get a lot of information including write & read speed. Compare your results to Know the performance of your hard drives.
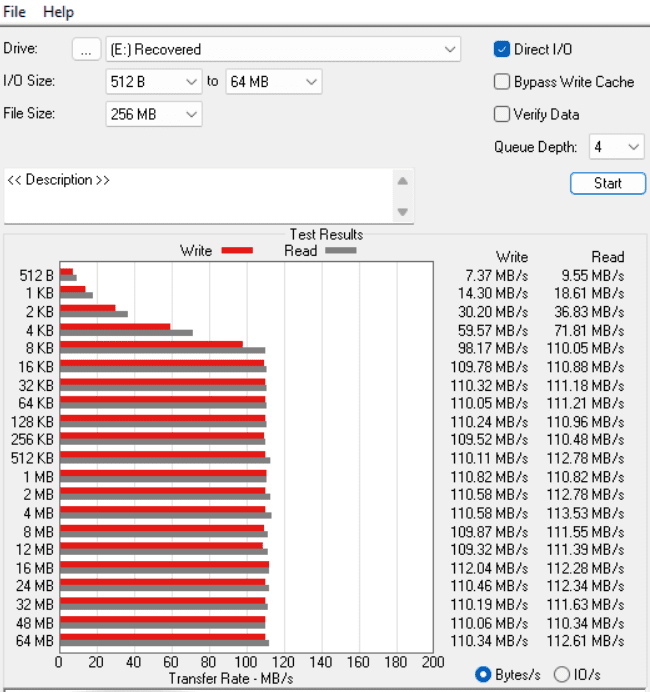
How to Test Hard Drive speed using 3rd party tools
While the command prompt provides a reliable method for tech-savvy users, third-party tools offer a user-friendly and feature-rich alternative. These tools cater to various technical levels and preferences, allowing you to choose the one that best suits your needs. Let’s explore some popular options for testing your hard drive speed with third-party tools:
1. CrystalDiskMark
- Download the Zip File of CrystalDiskMark from the official website.
- Right click on the Zip file and select “extract All” Option. Now the Zip file will be extracted to another folder.
- Open that folder in your device. In this, select “Diskmark 64”. The UI of crystal diskmark 64 will open.
- Then, Click the “All” button to start the test.
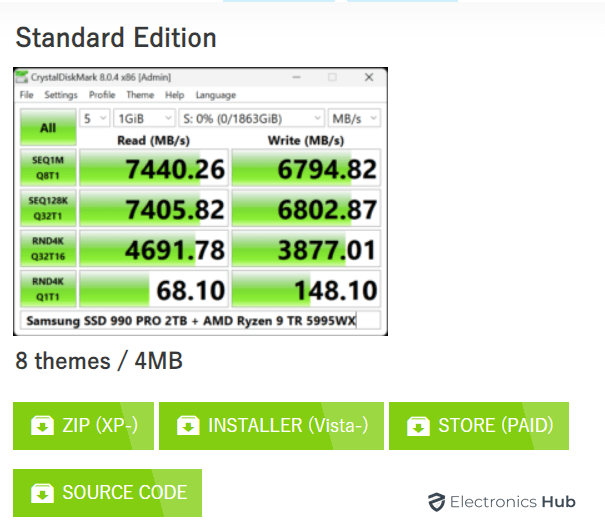
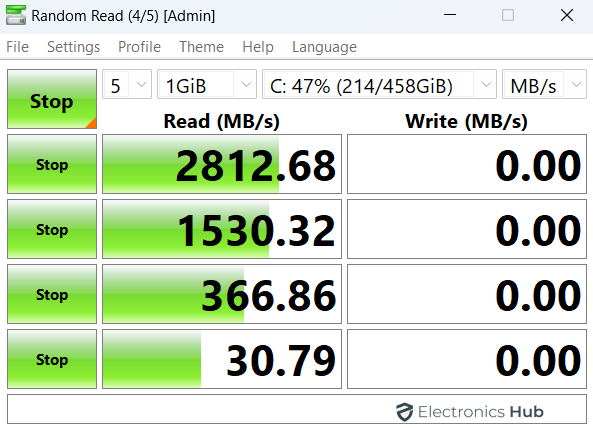
CrystalDiskMark will display the following results:
- Seq 1MQ8T1 Read & Write: The read and write speeds for sequential data with a queue depth of 8 and a thread count of 1.
- Seq 1MQ1T1 Read & Write: The read and write speeds for sequential data with a queue depth of 1 and a thread count of 1.
- RND4K Q32T1 Read & Write: The read and write speeds for small (4KB) random data with a queue depth of 32 and a thread count of 1.
- RND4K Q32T1 Read & Write: The read and write speeds for small (4KB) random data with a queue depth of 1 and a thread count of 1.
Compare these results to online benchmarks for similar hard drives to assess your drive’s performance.
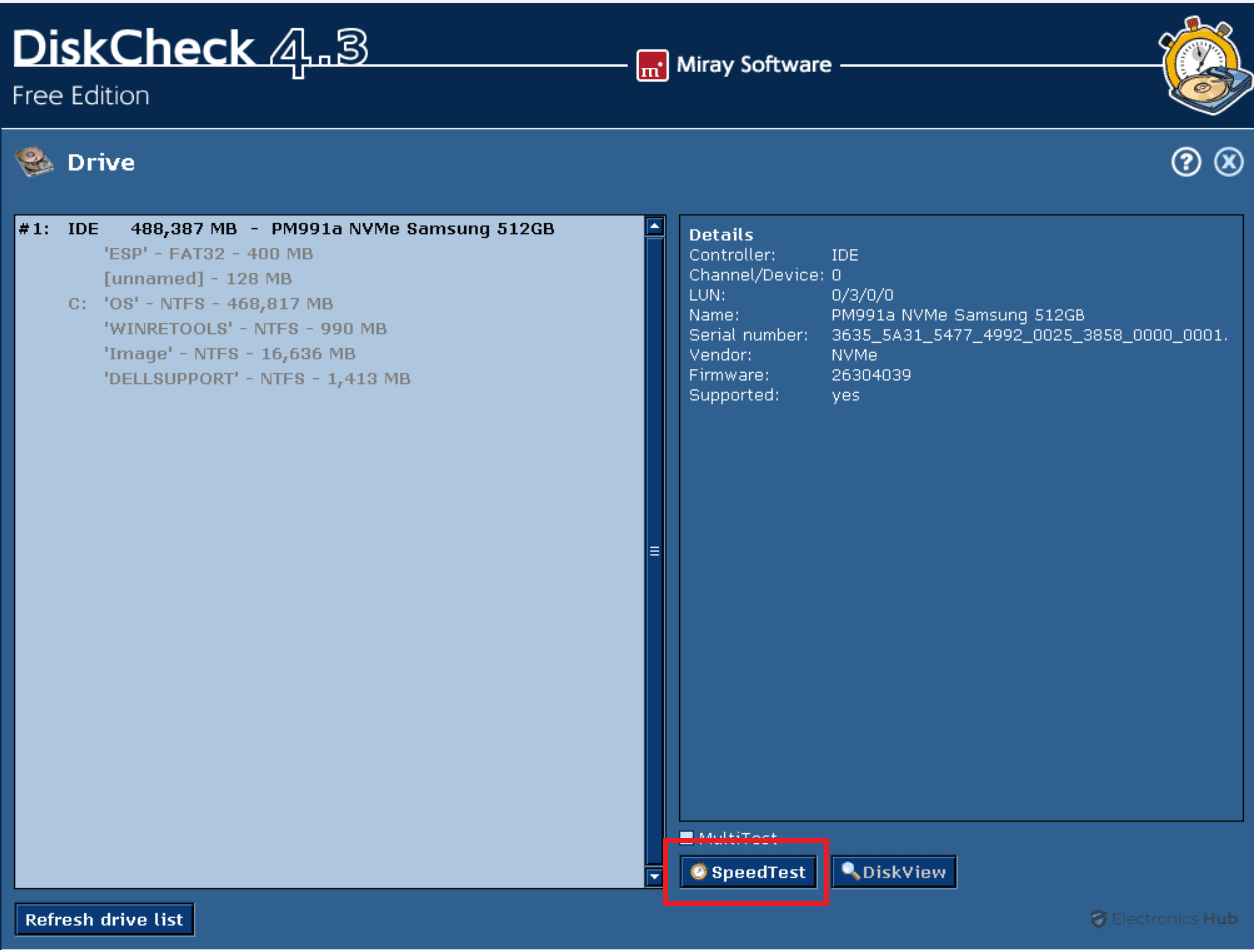
2. DiskCheck
- Download and install DiskCheck. then, Launch DiskCheck.
- Select the drive you want to test from the drop-down menu.
- Click the “SpeedTest” button.
- Wait for the test to complete.
- View the results, which include read and write speeds, I/O speed, and delay.
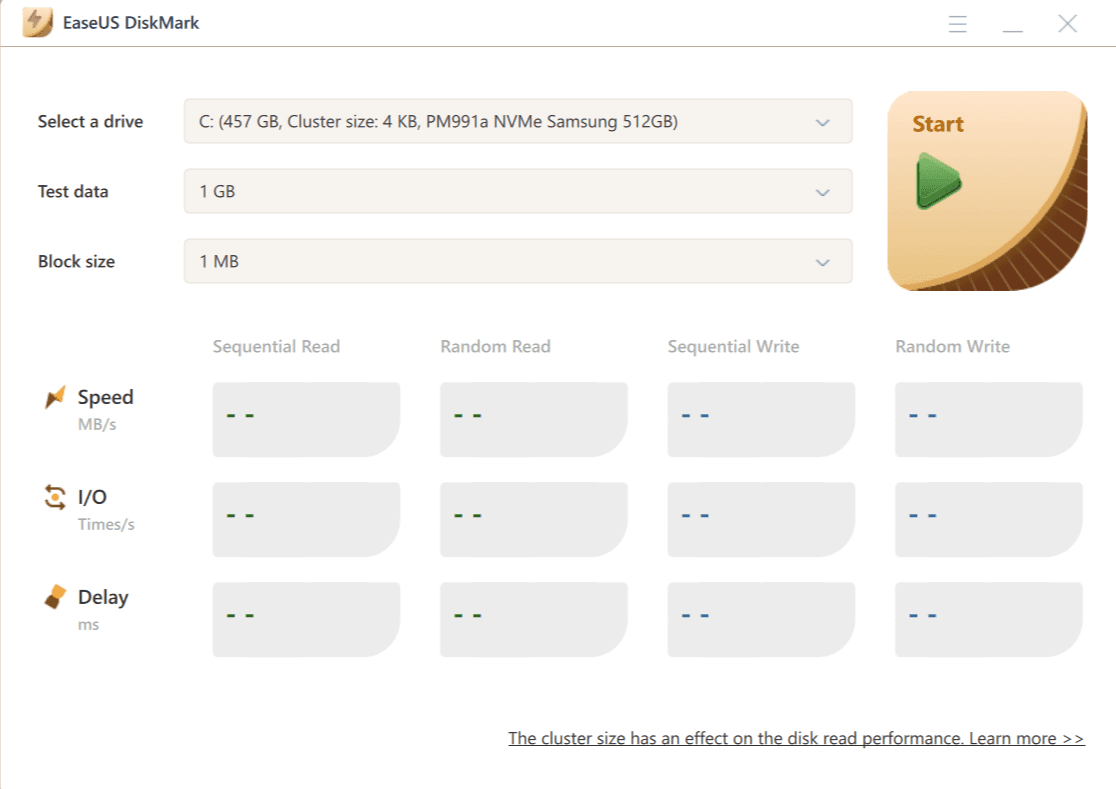
3. EaseUS
- Download and install EaseUS Partition Master.
- Launch the application and select your desired hard drive from the main interface.
- Click the “Disk Mark” button located on the top toolbar.
- Choose the test data size and block size from the drop-down menus.
- Click the “Start” button to begin the test.
- Observe the real-time read and write speeds displayed on the screen.
- Once the test is complete, analyze the results, including sequential and random read/write speeds, IOPS, and access times.
- Compare your results to online benchmarks for similar hard drives to get a sense of your drive’s performance.
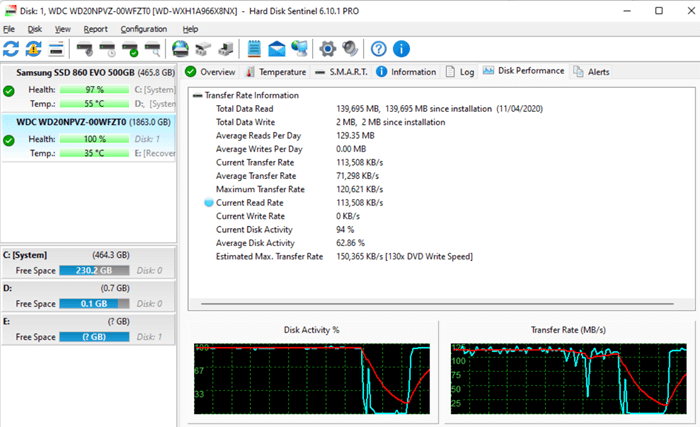
4. Hard Disk Sentinel
- Download and install Hard Disk Sentinel from their official website.
- Open Hard Disk Sentinel.
- Select your hard drive from the list of drives displayed.
- Click the Benchmark tab.
- Choose the desired benchmark test (e.g., Read, Write, Mixed).
- Click the Start button to begin the test.
- Wait for the test to complete.
- View your hard drive’s read and write speeds displayed in the results window.
- Compare your results to online benchmarks for similar hard drives or previous benchmarks.
5. Segue
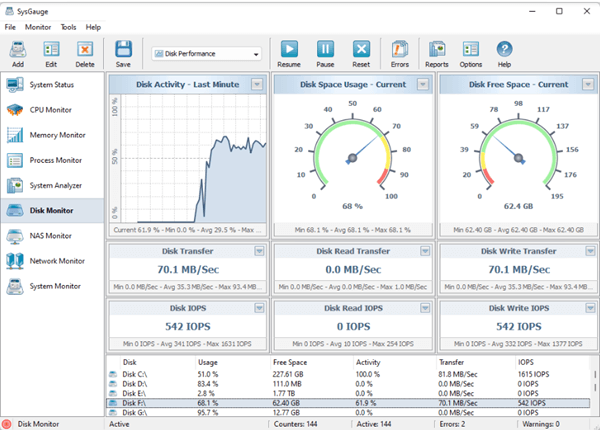
- Download and install SysGauge from the official website.
- Launch SysGauge and ensure it’s running as administrator.
- Click the “Add” button on the main toolbar.
- Select the “Disk Activity” counter category from the left-side view.
- Choose your desired hard drive from the middle view (default: all disks).
- Click “Start” to begin monitoring.
- Observe the real-time disk activity and transfer speed displayed in the SysGauge window.
- Optionally, you can export the monitoring results as a report in various formats (HTML, PDF, Excel, etc.) for further analysis.
6. Smartmontools
- Download and install Smartmontools.
- Open a command prompt as administrator.
- Navigate to the directory where Smartmontools is installed (e.g., “C:\Program Files\Smartmontools”).
- Type the following command and press Enter: smartctl -a /dev/sdX
- Replace “sdX” with the actual device name of your hard drive (e.g., sd0, sd1, sd2, etc.).
- Review the output, focusing on attributes like Read Error Rate, Reallocated Sectors Count, and Current Pending Sector Count.
- Consult the Smartmontools documentation or online resources to interpret the attribute values and assess your hard drive’s health.
7. PassMark Performance Test
Download and install PassMark Performance Test from their official website.
Launch the application and navigate to the “Disk” tab.
Select the hard drive you want to test from the “Drives” dropdown menu.
Choose the desired test options:
* Block size: Select the block size you want to use for the test. Larger block sizes generally result in faster speeds.
* Number of threads: Choose the number of threads to utilize for the test. More threads can improve testing speed but may impact system performance.
* Test duration: Set the duration for the test. Longer durations provide more accurate results.
Click the “Start” button to begin the test.
Once the test is complete, the results will be displayed on the screen, including:
* Read speed: The speed at which your hard drive can read data.
* Write speed: The speed at which your hard drive can write data.
* IOPS: The number of input/output operations per second.
Compare your results to benchmarks for similar hard drives to get a sense of your drive’s performance.
8. ATTO Disk Benchmark
- Download and install ATTO Disk Benchmark from the official website.
- Launch ATTO Disk Benchmark.
- Select your desired drive from the “Drive” dropdown menu.
- Choose the desired block size from the “Transfer size” dropdown menu.
- Set the test length using the “Length” bar.
- Click the “Start” button to begin the test.
- Observe the results displayed in the table.
- Analyze the read and write speeds for various block sizes.
- Compare your results to online benchmarks for similar hard drives.
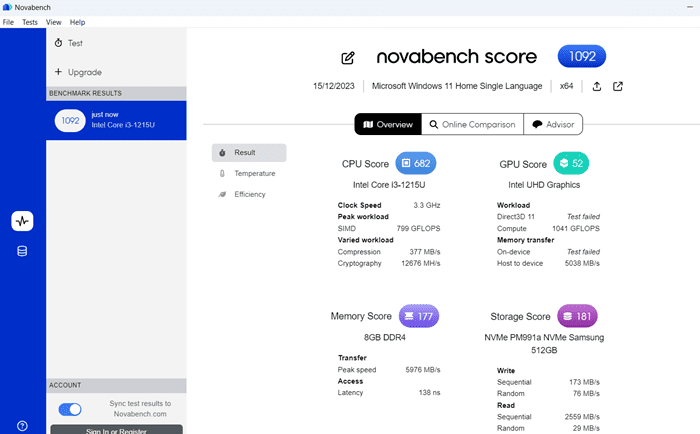
9. Novabench
- Download and install Novabench from the official website.
- Launch Novabench and click the “Run Tests” button.
- Select the “Disk” test category.
- Choose the specific drive you want to test from the drop-down menu.
- Click the “Start Test” button.
- Wait for the test to complete.
- View your hard drive’s read and write speeds displayed in the “Results” window.
10. Geekbench
- Download and install Geekbench 5 from the official website.
- Launch Geekbench and select the “CPU” benchmark.
- Click the “Run Benchmark” button.
- Once the benchmark finishes, scroll down to the “Disk” section.
- You will see your hard drive’s read and write speeds listed in megabytes per second (MB/s).
- Compare your results to online benchmarks for similar hard drives to assess your drive’s performance.
How to know Real time speed of hard drive
Go to the Task Manager.
- a) Windows 10: Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc or right-click the taskbar and select Task Manager.
- b) Windows 11: Press Ctrl + Alt + Delete and select Task Manager or right-click the Start menu and select Task Manager.
Click the Performance tab.
Locate your hard drive under the Disk section.
Observe the Active Time and Disk Activity graphs.
Active Time: Shows the percentage of time your hard drive is actively reading or writing data.
Disk Activity: Displays the real-time transfer rate of data to and from your hard drive.
Unleashing Your Hard Drive’s Potential: Optimization Tips
Once you’ve assessed your hard drive’s performance, it’s time to unleash its full potential. Implementing a few simple optimization techniques can significantly improve your drive’s speed and boost your overall computer experience. Here are some key steps you can take:
1. Defragment Your Hard Drive:
Over time, files on your hard drive become fragmented, impacting their access speed. Defragmenting your hard drive rearranges these fragmented files, allowing them to be read and written more efficiently.
a) Windows Built-in Tool:
- Open the “Defragment and Optimize Drives” tool.
- Select your hard drive and click “Optimize.”
b) Third-Party Tools:
- Many third-party tools like Auslogics Disk Defrag offer additional features and scheduling options.
2. Close Unnecessary Programs
Running multiple programs in the background can consume system resources and impact your hard drive’s performance. Close any unnecessary programs, especially resource-intensive ones, to free up resources and improve speed.
3. Disable Startup Programs
Many programs automatically launch at startup, slowing down your computer’s boot time and consuming resources. Disable unnecessary startup programs using the Task Manager or a dedicated startup manager tool.
4. Update Drivers
Outdated drivers can cause various performance issues, including slow hard drive speeds. Update your storage controller drivers to ensure optimal compatibility and performance.
5. Upgrade to an SSD
If your computer uses a traditional HDD, upgrading to a Solid State Drive (SSD) will provide a significant performance boost. SSDs offer much faster read and write speeds, leading to quicker loading times, smoother performance, and a more responsive experience.
6. Regular Maintenance
Cleaning up temporary files, defragmenting your hard drive regularly, and removing unnecessary applications can contribute to improved performance and prevent future issues.
7. Monitor Hard Drive Health
Utilize built-in tools like SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) or third-party monitoring software to track your hard drive’s health and identify potential problems before they become critical.
By implementing these optimization techniques, you can significantly improve your hard drive speed and ensure optimal performance for a smoother and more efficient computing experience.
Test Hard Drive Speed Windows – FAQS
Ans: Yes, HDDs can experience performance degradation over time due to factors like wear and tear, file fragmentation, and software issues. As the magnetic surface of the platters wears down and the read/write heads age, their ability to read and write data accurately and efficiently diminishes. Additionally, fragmented files across the disk require the heads to move more often, leading to slower access times.
Ans: The average lifespan of an HDD varies depending on usage, temperature, and brand. Typically, you can expect an HDD to last anywhere between 3 to 5 years. However, high-quality drives with proper cooling and moderate usage can last up to 8-10 years.
Ans: Unlike HDDs, SSDs have a different type of wear and tear mechanism. Their lifespan depends on the total amount of data written to the drive. Typically, consumer-grade SSDs have a lifespan of 5-10 years, while high-endurance SSDs used in enterprise environments can last several years longer.
Ans: Cleaning up your hard drive involves removing unnecessary files, programs, and temporary data. Here are some key steps: * Uninstall unused programs: Navigate to the “Apps & features” settings in Windows and uninstall any programs you no longer need.
* Delete temporary files: Use the Disk Cleanup tool or third-party software to remove temporary files and cache data.
* Clean up downloads folder: Empty your Downloads folder regularly to remove unnecessary files.
* Defragment your hard drive: This reorganizes fragmented files for faster access (applicable to HDDs).
Move large files to external storage: Transfer large files you rarely use to an external storage device to free up space on your hard drive.
Conclusion
Assessing the speed of your hard drive is a crucial measure in upholding computer health and optimizing performance. Through consistent monitoring and proactive measures, you can guarantee a seamless and efficient user experience. Keep in mind to select the testing method that aligns with your requirements and technical proficiency. For additional support, explore the array of third-party tools at your disposal.