In this tutorial, we will take a look at the concept of Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), what is the need for such “neural networks”, basic elements of ANNs and finally the applications of Artificial Neural Networks.
Outline
ToggleIntroduction
You might have heard the terms Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence and even Artificial Neural Networks in the recent times. All these are different ways of answering the good old question of whether we can develop a new form of intelligence that can solve natural tasks.
Computers have superior processing power and memory and can perform a severely complex numerical problem in a short time with ease. But when a real-world intelligent task associated with vision, speech, pattern recognition and natural language processing is presented, it falls short and shows its inadequacies.
This is because, computers, with or without Artificial Intelligence, need an algorithmic approach i.e. the problem must be presented as an algorithm and when a real-world problem task cannot be formulated as an algorithm, then the computers cannot do the same thing as our brains: learn and adapt.
Human brains are fascinating things and even the fastest computers cannot compete with the brain in one thing: our brains learn, analyze and explore the problem and finally adapt to the situation.
Keeping this biological aspect in mind, scientists are developing a several computer models that are inspired by Biological Neural Networks that can provide a path to solve the problems of natural tasks. This approach is known as Artificial Neural Networks or ANN.
What are Artificial Neural Networks?
Simply put, Artificial Neural Networks are software implementations of the neural structures of human brain. ANN is a computational system influenced from the structure, processing capability and learning ability of a human brain.
Not diving deep into the complex biology of it, let us take a look at the structure of our brain. Human brain contains billions of neurons that act as organic switches. All these neurons are interconnected to form a huge and complex structure called Neural Network. The output of a single neuron is dependent on inputs from thousands of interconnected neurons.
The “Learning” of a human brain is simply repeated activation of certain neural connections and this repetition strengthens the connection. So, for a specified input, the neural connections make sure that output is always a desired one. A simple feedback from the outcome helps the learning process as it strengthens the neural connections.
This behavior of the brain is key to Artificial Neural Networks as they simply try to replicate this action of the brain. This can be achieved in two ways:
- Supervised ANN
- Unsupervised ANN
Supervised Artificial Neural Networks
In Supervised Artificial Neural Networks, a matched input and output samples of data is provided to the network for training. The aim of this approach is to get a desired output for a specified input.
One of the best examples of a Supervised ANN is the spam filters of our e-mails. At training level, the input to the Artificial Neural Network engine would be a set of words in the body of the e-mail. The output is flagging the e-mail as either spam or not spam.
Unsupervised Artificial Neural Networks
The Unsupervised Artificial Neural Network is more complex than the supervised counter part as it attempts to make the ANN understand the data structure provided as input on its own.
Characteristics of Artificial Neural Networks
Any Artificial Neural Network, irrespective of the style and logic of implementation, has a few basic characteristics. These are mentioned below.
- An Artificial Neural Network consists of large number of “neuron” like processing elements.
- All these processing elements have a large number of weighted connections between them.
- The connections between the elements provide a distributed representation of data.
- A Learning Process is implemented to acquire knowledge.
Elements of Artificial Neural Networks
Keeping the above characteristics in mind, we can derive the basic elements of any Artificial Neural Network as follows:
- Processing Elements
- Topology
- Learning Algorithm
Let us take a brief look at these individual elements.
Processing Elements
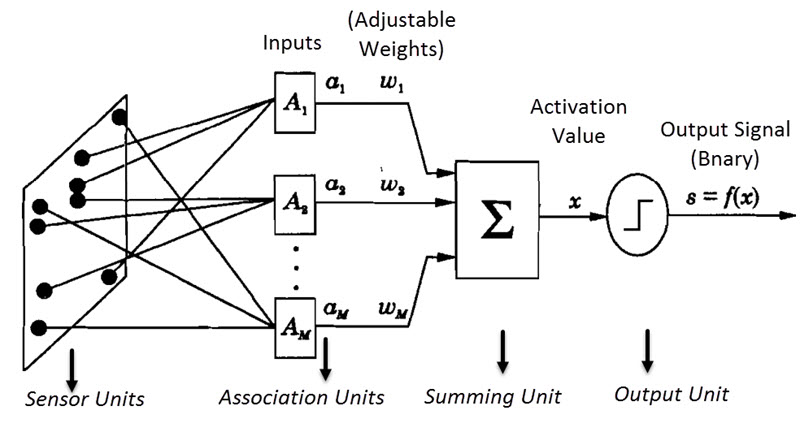
As the ANN is a simplified computational model of a biological neural network, an ANN consists of basic processing units or elements similar to that of neurons of a brain.
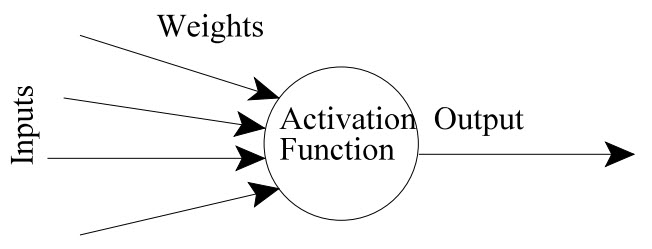
In general, a processing unit is made up of summing unit followed by an output unit. The function of a summing unit is to take n input values, weight each input value and calculate the weighted sum of those values.
Based on the sign of the weight of each input, it is determined whether the input has a positive weight or a negative weight. The weighted sum of the summing unit is known as Activation Value and based on the signal from this activation value, the output is produced.
Both the input and output can be either continuous or discrete as well as they can be either deterministic or fuzzy.
Topology
Any Artificial Neural Network will become useful only when all the processing elements are organized in an appropriate manner so that they can accomplish the task of pattern recognition.
This organization or arrangement of the processing elements, their interconnections, inputs and outputs is simply known as Topology.
Generally, in an ANN, the processing units are arranged into layers and all the units in a particular layer have the same activation values and output values. Connection can be made between layers in multiple ways like processing unit of one layer connected to a unit of another layer, processing unit of a layer connected to a unit of same layer, etc.
Some of the commonly used Topologies in Artificial Neural Networks are:
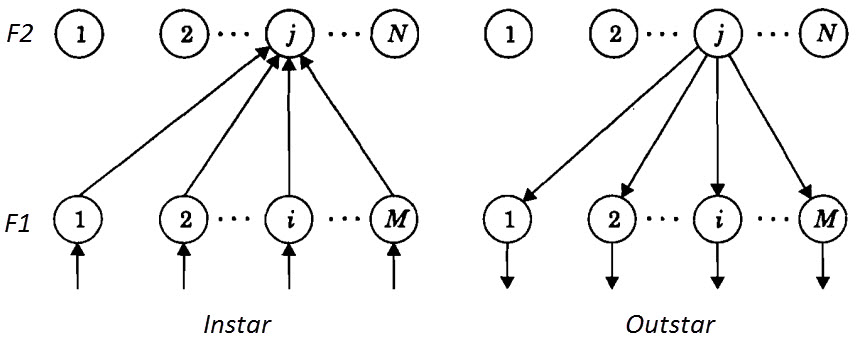
- Instar
- Outstar
- Group of Instars
- Group of Outstars
- Bidirectional Associative Memory
- Autoassociative Memory
The following image shows an arrangement of two layers F1 and F2 with M and N number of processing units each in both Instar and Outstar Topologies.
Learning Algorithm
The final and important elements of any ANN are Learning Algorithms or Laws. The operation any neural network is governed by Neural Dynamics consisting of both activation state dynamics and synaptic weight dynamics.
Learning Algorithms or Laws are implementations of synaptic dynamics and are described in terms of first derivative of the weights. These leaning laws can be supervised, unsupervised or a hybrid of both.
Some of the commonly known Learning Algorithms are:
- Hebb’s Law
- Perception Learning Law
- Delta Learning Law
- Wildrow & Hoff LMS Learning Law
- Correlation Learning Law
- Instar Learning Law
- Outstar Learning Law
Different Types of Artificial Neural Networks
There are many different flavors of Artificial Neural Networks. Some of them are listed here.
- Feedforward Neural Networks
- Feedback Neural Networks
- Competitive Learning Neural Networks
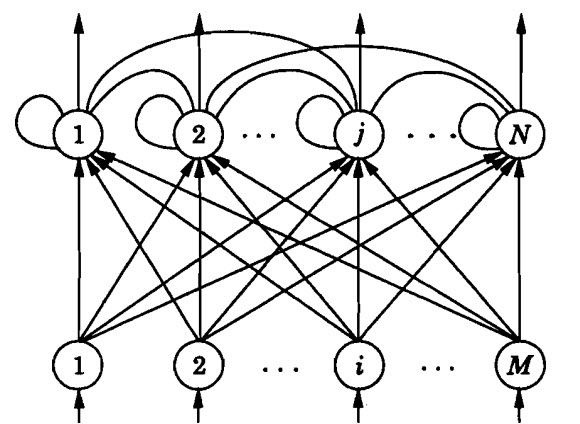
Feedforward Neural Networks
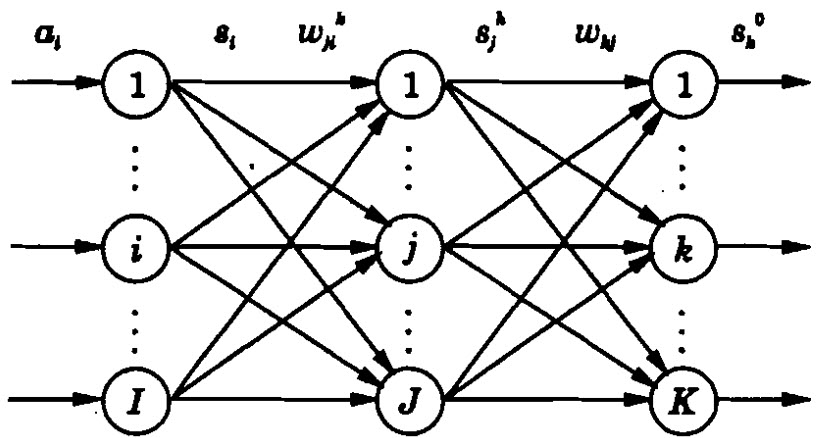
A Feedforward Artificial Neural Network, as the name suggests, consists of several layers of processing units where each layer is feeding input to the next layer, in a feedthrough manner. A simple two-layer network is an example of feedforward ANN.
The following is a simple structure of a three-layered feedforward ANN.
Feedback Neural Networks
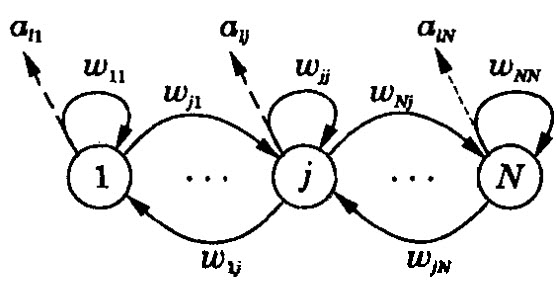
A feedback ANN consists of the feedback element. In a basic structure, a feedback ANN consists of a set of processing units, whose outputs are fed back as inputs to all other units of the same layer including the same unit.
In its basic form, a feedback ANN doesn’t have any structure and hence it is not an useful at pattern recognition.
Competitive Learning Neural Networks
It is a combination of both feedback and feedforward ANNs. The input layer is linear and its outputs are given to all the units in the next layer.
The outputs of the second layer can be either linear or non-linear (depending on the application).
Advantages
- The main advantage of ANN is parallel processing. This makes it more useful that linear programs.
- Due to their parallel processing structure, any failure in one neural element will not affect the rest of the process.
- Neural networks can be applied to any application and they can solve any complex problem.
- By implementing appropriate learning algorithms, an ANN can be made to learn without reprogramming.
Disadvantages
- All the parallel processing requires a huge amount of processing power and time.
- There is a requirement for a “training” period before real-world implementation.
Applications of ANN
The two important areas where ANNs have a huge potential of applications are Speech and Image Processing.
Applications in Speech
- Vowel Classification
- Recognition of vowel-consonant segments
- Recognition of stop consonant-vowel utterances in Indian languages
- Nettalk
- Phonetic Typewriter
Applications in Image Processing
- Recognition of Symbols (used in Olympics)
- Recognition of handwriting
- Segmentation of image
- Classification and segmentation of texture