PC components generate heat while they are operational. While some components like RAM, HDDs and SSDs do not generate considerable heat, the CPU and GPU get really hot while working under heavy load. This includes gaming, video rendering, and other heavy tasks. To get the best performance from your system, you need to monitor the temperature level of your components closely and make sure the temperature levels stay within design limits.
In the case of a GPU, you will get continuous stuttering and even crashing of games or other software if your GPU is overheating. If you are facing the same problems, you have come to the right place. Today, we will try to understand why GPUs get hot while they are functioning and how you can check the temperature levels. We will also give you some tips on how you can maintain the temperature levels under a design limit.
Outline
ToggleReasons Behind High GPU Temperature
GPUs, just like other PC components, get hot when you are using it under heavy load. The rise in temperature is caused by the internal electrical resistance of the circuitry of a GPU. As GPUs are continuously connected to a power supply, the resistance keeps on increasing the working temperature of the GPU at a steady rate. And when you start a heavy process, the power draw of the GPU increases and you will notice a sudden rise in temperature.
Although, GPUs are designed to work with a high-temperature range of about 80 to 90 degrees celsius. Thus, temperatures below 90 degrees celsius are pretty much standard for a high-end GPU while you are playing a similarly high-end game. But if you are noticing high temperatures even in ideal conditions, it means there is a problem with your GPU and you need to check the thermal performance right away.
Monitoring your GPUs Temperature
Checking your GPUs temperature levels is a fairly easy process. All you need to do is follow one of the solutions given here to get real-time monitoring of your GPU temperature levels. In case you are wondering how it works, there are thermal sensors available in your system that monitor the temperature levels and operate the cooling fans accordingly. By following the methods given here, you are simply noting the responses from these thermal sensors.
1. Windows 10 Task Manager
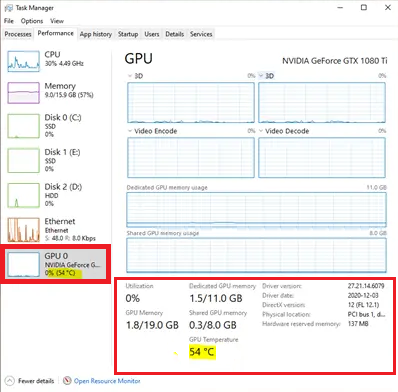
Windows has a built-in tool for resource monitoring and management called the task manager. Here, you can check all the active processes in your system, their resource consumption, and the performance of the installed components. Here’s how you can check the temperature of your GPU from the task manager:
- Press “Ctrl+Shift+Esc” together to open the task manager.
- Click on “More details” to expand the task manager.
- Now, head over to the “Performance” tab.
- Here, you will see the details of all the components installed in your system. Below the GPU, you will find the make and model of the card along with the real-time temperature levels.
- You can click on the GPU to know additional parameters such as power consumption and memory usage.
2. Through Your GPU’s Control Software
If you wish to get more detailed statistics about your GPU such as clock speed and fan speeds apart from the temperature, we recommend you to use the system monitoring software designed by the manufacturer of the graphics card. Almost all GPU manufacturers offer a dedicated program to monitor these parameters.
With the dedicated system monitoring software, you will be able to check all of these parameters with the options to control the function of the hardware as well. This includes changing the core clock or memory clock of the GPU, controlling the fan speed, and adjusting the voltage and power limit based on your requirement. You will also find predefined modes on the software, which makes things even easier for the user.
3. 3rd Party Software
Apart from the methods mentioned above, you can also use dedicated 3rd party software to check the temperature of your GPU. There are a variety of programs that serve the purpose of monitoring the advanced parameters of the GPU. Programs such as HWinfo, GPU Temp, Open Hardware Monitor, etc., will certainly be helpful in this scenario.
Apart from the basic core temperature, you will also get to know the hot spot temperatures, core voltage level, power consumption, and clock speeds, and tonnes of other parameters from these 3rd party software. It is essential to monitor these parameters in real-time to understand the working of the GPU and the specific program which causes sudden temperature rise.
Average GPU Temperatures
As we mentioned earlier, most GPUs have designed temperature limits that are considered to be safe while the GPU is functional. It changes from model to model based on the manufacturer, the capacity of the GPU, and the model. To be specific, there are OC-supported GPU models which ship with better active cooling fans and offer a higher temperature range.
In any case, you should keep the following temperature levels in mind as the average performance of your GPU needs to be in this range for best results.
- In idle conditions, your GPU must offer 30° to 50°C temperature levels. It depends upon the cooling system installed in your cabinet as well as the ambient temperature.
- When under heavy load, the GPU should perform under the temperature range of 65° to 90°C. In this case, the fans will be active at max capacity to maintain the temperature levels.
- As for gaming, the average temperature levels vary for different types of games. In the case of casual games, you should get about 60° to 75°C temperature levels while heavy games such as Cyberpunk 2077 or Microsoft Plane Simulator often run with more than 90°C temperature levels.
How GPUs are Cooled?
GPUs are designed to work with high temperatures as they handle more graphical load than your CPU and other components. Hence, manufacturers offer some onboard cooling peripherals on the GPUs to maintain the temperature levels.
This primarily includes fans on the GPU, which extract the heat from the core chip. There is also thermal paste on the units similar to CPUs to offer better heat exchange. Other than that, there are passive cooling techniques integrated into the design of the GPU, which includes copper heat pipes and metal fins. Let’s take a look at some more cooling systems used for graphic cards.
1. Open Air Cooling
A standard GPU powered by an open-air cooling system includes 1 to 3 fans included in its shroud. The fans offer forced air to extract heat captured in the aluminum heatsink for faster heat dissipation. You can control the performance of these fans directly from the manufacturer’s system software.
2. Blower Style Air Cooling
Blower-style air cooling is often seen in high-end graphics cards such as the Nvidia RTX 2080 or AMD Radeon RX 5700 XT. The key difference between the blower-style cooling system and the open-air cooling system is the radiator installed on the graphics card. The blower fan on these cards intakes air from the surrounding area and pushes it through the radiator for heat exchange.
3. AIO Cooling
AIO systems are quite popular for cooling CPUs and GPUs alike as they utilize both air and cooling liquid for heat dissipation. In this design, fans are installed to cool both the radiator and heatsink of the GPU. But, there is also a cooling liquid introduced in the system which cycles between the cold plate and the radiator of the GPU. You can get a 3rd party AIO hybrid cooling system specifically designed for your GPU.
4. Liquid Cooling System
Finally, there is the most advanced and effective liquid cooling system for controlling the temperature levels of the GPU. It is a pretty straightforward system in which heat is directly extracted from the components of the graphics card for faster effect. While it is the most effective system, it is also quite expensive and requires an experienced professional to install to avoid further problems.
Factors That Affect GPU Temperature
Apart from the lead on the GPU, there are some additional factors that also affect the temperature levels of the GPU. This includes internal as well as external factors which we will cover in this section of our guide.
1. Ambient Temperature
The ambient temperature is probably the most important factor in this scenario. For proper heat dissipation, the surrounding temperature in your region must be lower than the working temperature levels of your GPU. As the ambient temperature increases, the speed of heat transfer reduces which further brings down the performance of the cooling system.
2. Cabinet & PSU
While building a desktop system, you must keep in mind that the size and form factor of your system also affects the cooling performance of your GPU. If the case is compact, you can only install 1 or 2 fans in the cabinet. Also, there is not a lot of space available for an ample amount of airflow in the cabinet, which also causes temperature rise.
As for the PSU, you should pick up an option that has an 80 plus rating and offers better efficiency. Low-efficiency PSUs cause further increases in the temperature levels of the cabinet, which in turn affects the cooling performance of your GPU.
Is My GPU Too Hot?
Now that you have a basic idea about the average temperature levels and cooling systems installed on the GPUs, let’s try to understand what temperature levels should be considered too hot for the GPU. As there are a lot of GPU models available in the market, the working temperature levels are also different. Hence, a certain temperature might be too hot for one unit while being average for the other.
1. Nvidia
Graphics cards designed by Nvidia are hugely popular in the market. These graphic cards are designed to operate under a working temperature range of about 50 to 90°C. There are high-capacity GPUs from Nvidia, such as the RTX 3070, RTX 3080, and so on that often work at 95°C or above. Therefore, a temperature level of about 100°C should be too hot for Nvidia GPUs.
2. AMD
AMD is slowly capturing the market with its new generation of high-capacity graphic cards. Similar to AMD CPUs, the AMD GPUs are also designed to withstand high thermal levels and come with better cooling systems. Up until now, even the budget options from AMD were powered by a blower-style cooling system. While the standard temperature levels for AMD GPUs can be around 60° to 95°C, you can also expect more than 100°C without any problem. Thus, temperatures above 100 or 110°C should be considered too hot for AMD GPUs.
Problems With High GPU Temperature
A lot of GPUs are designed with internal fail-safe circuits for protection against overheating. This basically reduces the power draw of the GPU if the temperature exceeds the designed temperature limit of the card. Thus, you will notice a sudden drop in performance which will be recovered once the temperatures are in control.
And if the temperature levels keep going up even after throttling the power draw of the card, your computer will crash at some point as the graphic card stops responding. This is also a fail-safe to prevent damage to the graphic card or other components of your system in case of a sudden temperature rise.
How to Maintain Your GPU’s Temperature
Now that you know what high temperature can do to your GPU, let’s take a look at what you can do to prevent it. As GPUs are complicated PC components, it is quite difficult to pinpoint the exact problem that causes the rise in temperature. Hence, we have mentioned some routine techniques to manage the temperature levels of your card with ease.
1. Clean the Cabinet
To make sure your case is not the culprit in this case, simply open the case from the side and monitor the temperature levels. If the temperature levels seem to be in control, it is time to invest in a better case for your PC. But before that, you can also try cleaning the residue dust and dirt inside the system, which also causes throttling in the heat exchange rate.
2. Check The GPU Fans
While you are monitoring the internal part of your system, take a look at the fans of the graphics card to check whether they are functioning properly or not. If the fans are not functioning, the temperature levels of your GPU will keep on rising even at ideal conditions. Clean the fans provided on the GPU for better efficiency. If the fans are stopped, you need to send the GPU for servicing.
3. Check OC Settings and Fans
Overclocking causes a significant rise in temperatures as it increases the power draw of the GPU in order to offer better performance. Hence, we will only suggest you overclock your GPU if you have an AIO or liquid cooling system installed in your cabinet. You can check the OC settings in manufacturer software such as MSI afterburner and select the normal mode for better thermal performance.
4. Add More Case-Fans
If your case offers multiple slots for cabinet fans, you should utilize them all by adding more case fans in your cabinet. This increases the airflow in your cabinet, which will definitely result in better heat dissipation and better temperature levels on your GPU.
5. Replace the Thermal Paste
In case the average temperature levels of your GPU have been rising for a long time, it might indicate problems with the thermal paste. Similar to the CPUs, the thermal paste applied on the GPU might get damaged over time. By simply replacing the thermal paste on your GPU, you can expect a 10 to 20°C difference in average GPU temperature.
6. Maintain Lower Ambient Temperature
If you reside in a comparatively warmer region, there is only so much you can do to keep the temperature levels of your GPU in control. To get better temperature levels on your GPU, you should invest in a decent air conditioner to keep the surrounding ambient temperature low. This means the average room temperature where you have your system should be within 30 to 35°C
Conclusion
High-temperature levels on a GPU might cause a lot of problems. Apart from slower performance and frequency crashes, the overall lifespan of the GPU reduces if it is operated at a high temperature. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor these temperature levels and maintain the performance of the GPU at all times.
We hope that you have managed to find the root cause of high-temperature levels on your GPU. If you find the temperature levels too high for your GPU, make sure you follow the tips given in our guide to bring the temperature levels down to the design limit of the card.