Aluminum is one of the most popular metals that are used to make a wide range of commercial applications. Owing to its protective natural and lightweight property, they find application in aircraft, spacecraft, trains, ships, vehicles, electronic appliances, window frames, and much more.
Apart from these, aluminum has a special place in the welding industry, thanks to its non-corrosive natural and aesthetically pleasuring appearance. However, welding aluminum is not an easy task by far. This article deals with the welding of aluminum in detail, starting from challenges to solutions.
Outline
ToggleWhy is Aluminum Welding Difficult?
Aluminum is an ideal metal for different types of welds. But the welder should know about the techniques and skills required for aluminum welding. Aluminum welding is difficult as it is a very soft metal with a relatively high tendency for oxidation. While pure aluminum has a melting point of 650°C, oxides of aluminum have a melting point of 2037°C. Therefore, one has to prevent aluminum from getting oxidized.
Moreover, when in the molten state, aluminum tends to react with impurities, which leads to weak welds. Furthermore, aluminum has high thermal conductivity, due to which lack of precision in welding can lead to burnout. Therefore, it is quite clear that aluminum welding is difficult than welding with other metals.
The following list of the factors that make aluminum welding difficult.
- Oxide Layer – Pure aluminum has high reactivity with oxygen, and an oxide layer settles on the top of pure aluminum. This oxide layer has a significantly higher melting point than pure aluminum. To melt the top oxide layer, welders need to apply high heat to achieve that higher melting point. However, they need to be careful so that they don’t burn holes in pure aluminum that lies beneath the oxide layer.
- Impurities – Aluminum has high reactivity, due to which it can easily get contaminated during the welding process. It can react with dirt and air, which can alter the properties of aluminum. Apart from reacting with oxygen from air, it also reacts with hydrogen from water or damp air. Therefore, the welders have to take extreme care to clean aluminum and keep it in the pure state.
- Bubbles – As stated earlier, aluminum can react with hydrogen from various available sources. The chances of reaction with hydrogen increase highly in the molten state. When the metal solidifies, the hydrogen separates out, leaving behind bubbles. These bubbles lead to the welding part becoming porous and weak with time.
Best Way to Weld Aluminium
Even though aluminum welding is difficult, the welders do it perfectly using the right welding process. There are different techniques available to weld aluminum accurately, avoiding the common issues. Before that, the most important step is to prepare the aluminum correctly before welding. Here are the steps to prepare aluminum in the best way.
- Step 1 – Get a solvent such as acetone and use it to remove any deposit from the aluminum surface, such as oil, grease, and droplets.
- Step 2 – Use a stainless steel wire brush to get rid of the oxide deposits on the aluminum surface. You can also use a moderate acid or a strong alkaline. Make sure that the surface gets fully dry before welding.
- Step 3 – Keep the aluminum dry all the time and store it at room temperature. Make sure that you use it within a few days so that you can use it in the pure state.
- There are various types of welding methods available for welding aluminum. GTAW/ TIG welding is the best among them. More about the welding types are discussed below.
Types of Aluminum Welding
The following is the list of the different types of aluminum welding commonly used.
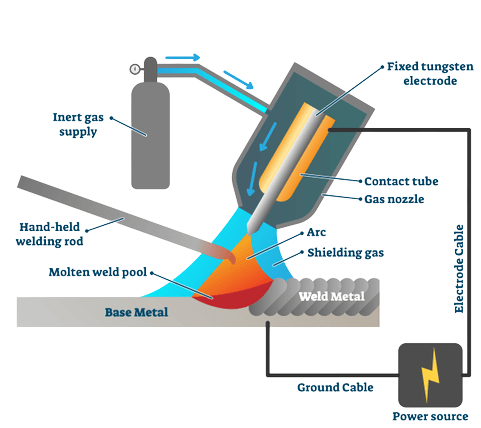
1. GTAW/TIG welding
GTAW stands for Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, and TIG stands for Tungsten Inert Gas welding. It is probably the most used welding technique by professionals for aluminum. In this process, the welder needs a constant current equipment with alternating current supply. It uses Argon as the shielding gas. The process automatically cleans the oxide layer from the surface of aluminum during welding. Therefore, there will be no contamination or impurities during the entire welding process.
Important Points To Keep In Mind:
- Use a pure tungsten rod as an electrode for the best result.
- Spend enough time in preparing the aluminum as stated earlier.
- Make sure that the argon flow is moderate and uniform to avoid irregular welding.
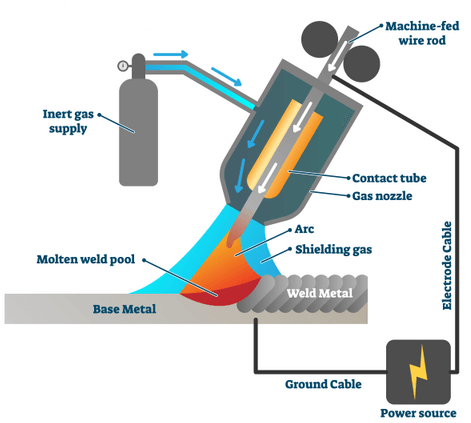
2. GMAW/MIG welding
GTAW stands for Gas Metal Arc Welding, and MIG stands for Metal Inert Gas welding. This is another most commonly used commercial process for welding aluminum. Compared to TIG welding, it is relatively faster, and the deposition rate is higher. The drawback is the use of a mechanical wire feeding system. Moreover, the welder has to make sure that the base material and filler are clean to avoid porousness after welding.
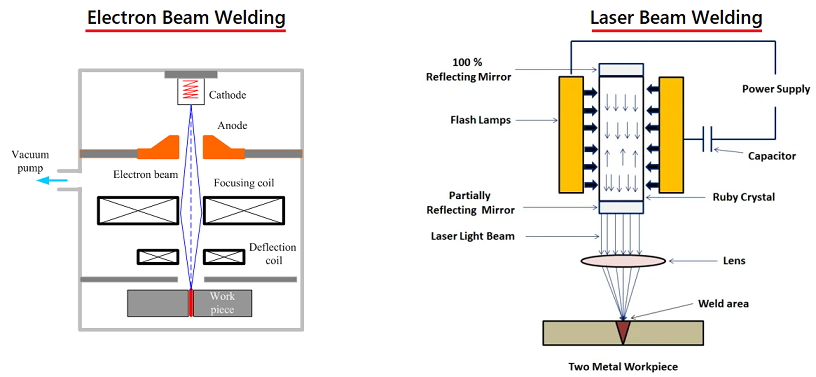
3. Beam welding
There are various beam welding processes available. For aluminum welding, laser beam and electron beam welding are popular. In electron beam welding, you can precisely heat only the targeted zone, and therefore, it offers more control on the overall process. It is suitable when you have thick aluminum sections for welding, and it does not need shielding gas as it takes place in a vacuum.
On the other hand, laser welding is faster, and it results in a narrow heat-affected zone. It is ideal for crack-sensitive materials like aluminum. However, the shielding gas selection has to be proper for longevity depending on the aluminum grade.
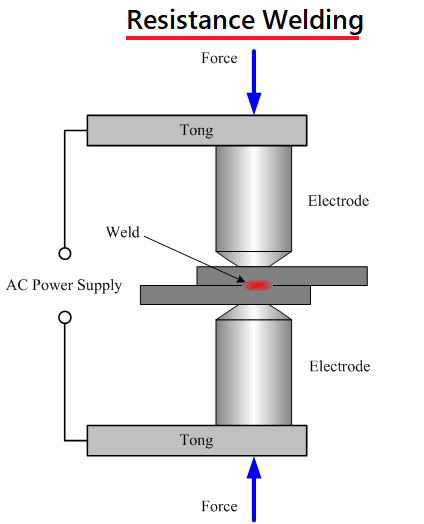
3. Resistance welding
In this process, metals are joined by passing current under high pressure. This is not a common process as aluminum has high electric and thermal conductivity. A welder has to be very skilled and precise with specifications for the welding to be good enough.
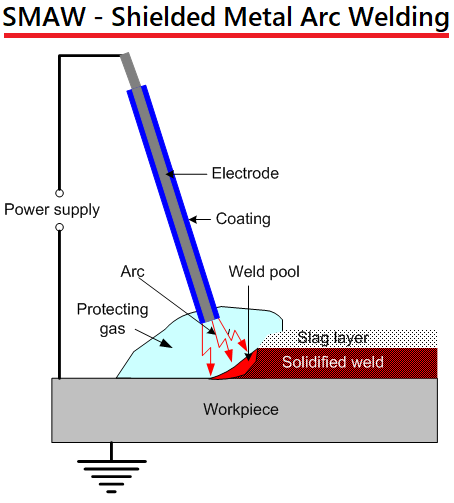
4. Shielded metal Arc
In this process, the welder uses a consumable aluminum electrode. The electric current forms an electric arc in between the joining metal and electrode. With time, the electrode and the metal melt to form a molten pool, which is cooled to form the joint. This aluminum electrode comes covered with a flux, which acts as a protecting or shielding gas when the electrode melts. Therefore, the weld part gets protection from weather conditions. Though it is not a common welding process, it is perfect for modifying cast aluminum.
Things to Avoid When Welding Aluminum
Here is the list of common mistakes to avoid while welding aluminum.
- Not Taking Safety Measures – Welding is a risky process no matter how experienced you are. Therefore, take all the possible safety measures like wearing a PPE kit. The PPE kit consists of goggles, welding helmets, safety gloves, and protective shoes. There will be a lot of sparks and splatters, and harmful fumes, that’s why you must cover your body properly.
- Not Doing Proper Preparation – Preparation is important for both welder and the welding material. We have already stated how to prepare aluminum before welding. It should be thoroughly cleaned and protectively stored. Similarly, the welder should be aware of the welding method for aluminum beforehand. He should not be confident just because he has experience in welding other metals.
- Not Taking Attention To Details – When you are dealing with sensitive material like aluminum, you have to be patient and pay attention to details. A minor mistake is enough to turn welded part fragile and porous. There is no scope for a misstep in aluminum welding.
Benefits of Using Aluminum
There is no doubt that welding aluminum is difficult, but there is no replacement for aluminum in the industry. The benefits of aluminum are unmatched by other metals, and they are listed below.
- Lightweight – The biggest benefit of aluminum as a metal is its lightweight. It weighs comparatively less than steel, which is the most popular metal for welding. Aluminum has a better strength-to-weight ratio. Therefore, its lightweight property does not make it less strong. It is also easy to transport and convenient to handle.
- Durability – Unlike steel and other metals, aluminum is corrosion-resistant. There is no question of rusting, and it is weather-proof. As a matter of fact, it is non-reactive to UV rays, and hence, durability increases immensely.
- Flexibility – Aluminum can take any shape as required in the industrial process. Starting from rolling, extrusion to forging, and casting, all these processes are easily applicable on aluminum.
- Miscellaneous – Aluminum is easily recyclable, and it has a rather aesthetically pleasing appearance. Aluminum has electric and heat conductivity. It is fire-resistant and needs minimal maintenance.
Conclusion
Aluminum is a very popular welding material in every industry. The welding process is no doubt difficult, but with enough practice, it can be mastered. To get the best results, you should pay attention to details and be active throughout the process. Hope you will learn something from this article.