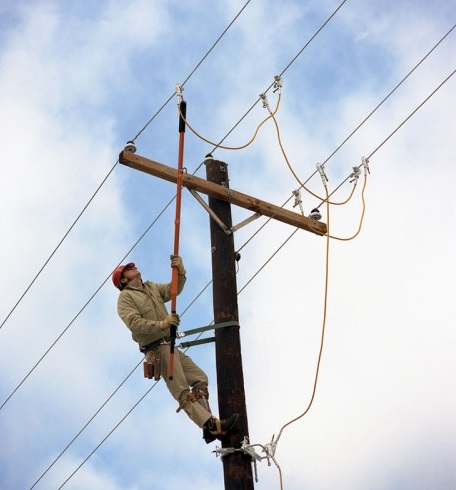
Nowadays, we often observe in newspapers and electronic media that many accidents are taking place involving electric hazards which even caused to the loss of many lives and property. The occurrence of these hazards is due to several reasons like equipment failures, human errors, weather conditions and fire accidents, etc. In the recent survey, most of the fatal accidents are caused by human errors like contact with electrical conductors like overhead power lines, bus bars and so on.
These electrical shocks or accidents not only cause severe injuries or death to people, but also damage the property and installations. Therefore, electrical safety is the necessary key to reduce such accidents caused by the electricity. So this furnished information is provided to give a complete description of electrical safety for a healthy and safe workplace.
Outline
ToggleWhy Electrical Safety Is Important?
Before going to know about different common electrical hazards, adverse effects to humans and property, safety devices and precautions we have to aware of the importance of having electrical safety. Electrical hazard can result to burns, electrocution and shock. If the adequate precautions and necessary safety procedures are not taken in a workplace, then adverse effects will occur to the workers. With uncontrolled exposure to the electricity causes to kill personnel and even permanent or severe injuries.
In most of the cases the electrical hazards cause to complete loss or damage of heavy equipment, electrical appliances and other workplace properties. In industries, these are even cause to loss of work time, interruption to the regular work, increasing of worker’s compensation and so on. That’s why the electrical safety is so important in all aspects of life to provide a safe and secured environment in the workplace.
Common Electrical Hazards and Its Affects on Human Body?
There is a chance of shock or threat with all electrical equipment operations because electrical workers are exposed to the hazards associated with electricity faults and abnormal conditions. In general, these electrical hazards are categorized into shocks, burns and electrocutions.
1. Electrical Shock:
When body becomes the part of a path through which electric current flows in a closed path of the circuit then the electric shock occurs. This electric shock happens when
- The body get contact with conductors in an energized circuit.
- The body provides a path between conductor of an energized circuit and the ground.
- The body gets contact with a metallic part that has contact with energized wire.
Electric shock severity depends on the factors like amount of current flowing through the body, the path through which current flows in the body and the length of time a body subjected to the current. Resistance and potential difference are the two factors that decides the amount of current flow through the body. A low current on the body results temporary mild tingling sensation and sometimes even it causes of death.
The following can cause to humans in an experience of electric shock
- It can stop the breathing muscles or the heart, or both
- Due to the heating effect severe burns will come where the electricity enters and leaves the body
- It may cause breathing difficulty, ventricular fibrillation, bleeding, etc.
- Sometimes it causes to hit or strike something that are in work platforms in response to the shock
| Below 1mA | Generally not perceptible |
| 1 mA | Faint Tingle |
| 5 mA | Slight shock felt, not painful but disturbing; average individual can let go; strong involuntary reactions can lead to other injuries |
| 6 to 25 mA (women) | Painful shock, loss of muscular control |
| 9 to 30 mA (men) | The freezing current or let-go range; individual cannot let go but can be thrown away from the circuit if extensor muscles are stimulated. |
| 50 to 150 mA | Extreme pain, respiratory arrest, severe muscular contractions; death possible |
| 1000 to 4300 mA | Rhythmic pumping action of the heart ceases; muscular contraction and nerve damage occur; death likely |
| 10000 mA | Cardiac arrest, severe burns; death probable |
Ohm’s Law to Understand the Effect of Current on the Human Body
Basic rules of electricity will help to analyze electrical hazards on human body such as ohms law. Ohm’s law states that one volt will cause to current flow of one ampere through one ohm resistance. Therefore the voltage is the important factor that determines the current flow through a body resistance. Basically, the human body is also a resistor and its resistance is measured in ohms. Human body resistance is not fixed, but it varies from time to time and person to person. Human body resistance of various parts is
- Dry, intact (no cuts or scabs) skin 100 – 600 Kilo ohms
- Wet skin 1000 ohms
- Within the body 400 ohms
- Ear to ear 100 ohms
Thus, the resistance of a wet skin is much lesser than the dry skin therefore, more current will flow through the human body when it is wet.
2. Burns
These are the most commonly happened shock-related injury. This may occur when a person get contact with electrical wiring or equipment that is improperly maintained. Although these burns can occur anywhere on the human body but, typically such injuries occur on the hands and feet.
3. Electrical Arc Blasts
These hazards are commonly occurring due to the high ampere currents arcing through the air. The arcing faults are caused due to the equipment failures, improper placing of tools, improper use of equipment and the conduction of electrical current due to the foreign particles present in the air. If the arcing currents are at higher levels, these can cause fires and injuries. These arcs can be extremely high energy or low energy arcs, extreme one damages the equipment resulting in fragmented metal to fly in all directions, whereas the low energy one cause blasts in atmosphere by releasing explosive gases, combustible dusts and vapors.
The following can cause to humans due to the electrical arcs
- Most of the times electrical arc releases thermal radiations. Due to this thermal energy person get injured where the part of the body exposed to it. The degree of injury depends on the skin exposed, skin color, type of clothing wear, etc. To avoid the chances of getting injuries person must wear proper clothes, should maintain work distance and other over current protections.
- A high energy arc can produce a definite pressure ware that causes a serious ear damage and some instances it can lead to memory loss. This pressure wave could also propel or force a victim from the arc blast that in turn lead to a physical injury.
- A high energy arcs releases the droplets of molten metal by melting the copper and aluminium parts of electrical equipment. These droplets with high temperatures causes serious burns on human body which effect is much worse than injuries happened with other electrical hazards.
There is no particular equipment available to protect against the effects of blasts completely. But safer practices like while operating a breaker person must stand at the hinged side of a cubicle door, usage of protective clothing flash suits, always staying as possible as far from high voltage equipment etc. reduce burns from the arc blasts.
Protection Against Electrical Hazards
As we discussed up to now that electrical hazards result from unsafe installations or unsafe environment or unsafe work practices. We can avoid these hazards by the use of insulation, electrical protective devices, safe work practices, grounding and guarding.
1. Insulation:
Some of the insulators such as mica, glass, plastic and rubber are used to coat the conductors and other metals to reduce the flow of current. This insulation prevents the shocks, short circuits and fires. Therefore, it is a good idea to check the insulation of exposed wires for any defects before connecting the electrical equipment to the power source.
2. Guarding:
This involves in enclosing or locating electrical equipment so that people don’t come closer to the equipment frequently. These guarding locations can be rooms, vaults, etc. In addition to the enclosers, permanent screens and sign boards like ‘Danger’, ‘Caution’ and ‘Warning’ can serve as an effective guarding system.
3. Grounding:
Grounding is nothing but an intentional creation of a low resistance path for the current flow to the earth. Therefore, grounding diverts the high voltages in the event of fault occurrence so that it protects humans as well as equipment from electrical hazards. Although it does not guarantee that grounding completely prevents the shock or injuries to the personnel, however it reduces the risk from high voltages.
Therefore, while working with electrical equipment, grounding furnishes a second path for the current that in turn safeguard the equipment operator.
4. Circuit Protection Devices:
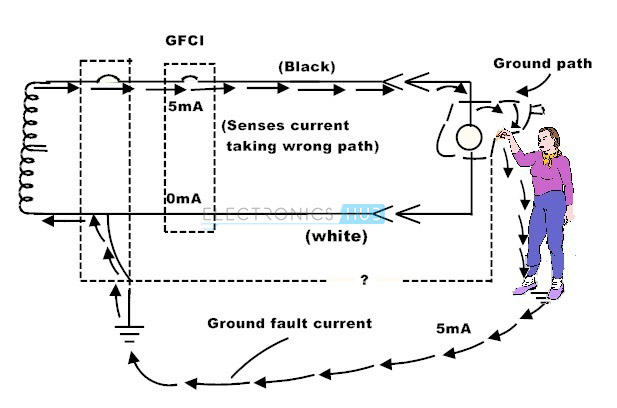
These devices protect the personnel as well as equipment in the event of any electrical fault by limiting or stopping the flow of current through the wiring system. These protection devices include circuit breakers, fuses, ground fault circuit interrupters, arc quenching devices, etc. These devices automatically shut off or de-energize the circuit when any fault takes place in the system.
5. Work Practices:
Safe work practices are the major accidental preventable methods in an electrical system. Some of these work practices are de-energizing of electric equipment before any repair or inspection, maintaining electric tools by placing in a proper place, remembering all the cautions especially working near overhead lines, usage of suitable protective equipment and so on.
Electrical Emergencies
As we discussed above electrical accidents cause numerous severe injuries and even to the death. These accidents are uncertain that means they can happen at any time or place. Quick response with proper rescue techniques to these accidents could save certain loss got by it. Very often in the event of electric shock, due to muscle clamping, victim cannot move or release the conductor. Thus, emerging response to save the victim minimizes the danger that could happen to the him. Some of the emergency rescue techniques are given below.
Approaching the Accident:
Assess the situation, but never rush into the accident place. Determine safer zone by keeping your self protective from the fallen wires and other accidental prone devices. Call the local electric utility and ask them for necessary action before they come. Carefully approach the accident area.
Examining the Scene:
Examine victims visually to determine whether they are in touch with live conductors or any metal objects. If you touch the energized victim or any conductive part it is possible that you may also become a victim therefore, don’t touch the victim unless he is de-energized. Try to de-energize electrical circuits by opening circuit breakers and unplugging equipment from power source.
Hazards Precautions:
Make sure that your hand and feet are dry and always stand on clean dry surface. Try to wear protective gloves and overshoes while removing the victim from the energized conductor with a non-conducting material.
Rescuing the Victim:
Unless the power is off do not lay a hand on the victim or near conductive material. If the power is off, then try to separate him from that area and start the first aid. In such situations, victim requires Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR). If the victim is normal like breathing and heartbeat is ok ,then try to give first aid for injuries. Ensure the medical care to the victim as soon as possible and take him to the medical doctor.
Grounding Concept of a Safe Circuit Design
A safe work environment against electrical hazards is created by ensuring the protection of personnel, equipment and facilities. Therefore, when considering the protection, proper grounding comes into the picture. An efficient grounding can fast enough to eliminate the damage or at least minimize damage when the fault occur in an electrical system.
Generally grounding refers to connecting a portion of an electrical circuit to earth. It is an intentional connection to earth from equipment or any electrical system. This grounding connection must be of sufficiently low impedance and have a capacity to carry the current to prevent the higher voltages in the time of electrical hazards.
Grounding in the electrical system is classified into two categories: System grounding and Equipment grounding. In system grounding one of the current carrying conductor is connected to the earth or ground. This grounding is used for surge and lightning protection which limits voltage across system components at safe value.
In equipment grounding all of the current carrying metallic bodies of equipment enclosures, raceways, conduits are connected to the ground. This is mainly provided to prevent the appearance of any voltages on the equipment enclosures so that the serious shocks or electrocutions to the personnels are prevented.
Grounding Practices
These practices maximize the personal safety by ensuring proper grounding methods by using appropriate grounding equipment.some of these practices are described below.
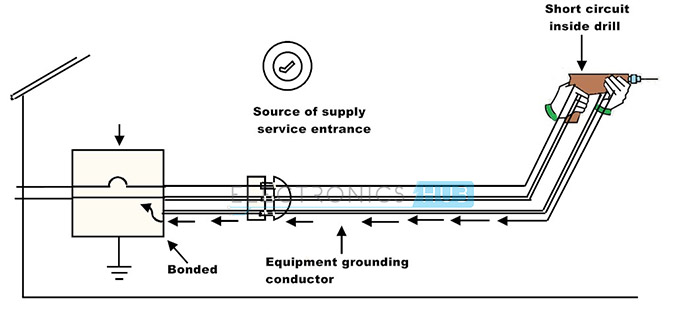
Grounding at Service Entrance Connection
For an effective grounding system, grounding must be located at the main service entrance. Here the neutral point of the power supply source is connected to the grounding conductor point. Further, this ground conductor is connected to the building ground point so that it ensures safety by maintaining equal potential to the all the conductors connected to it. This safety ground provides the necessary ground fault return path to the neutral point of power source.
Safe Grounding
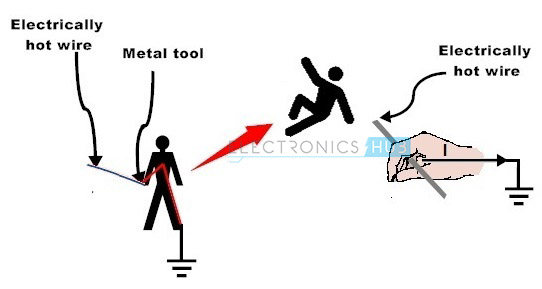
To provide safety to the personnel, equipment and system components, all the equipments must be referenced to single-point of the earth which is also called as single-point grounding. This is an effective and safety type of grounding compared with multi-point grounding. This minimizes the potential difference between any equipment, thus avoids hazards. We can observe in below figure that the current flow through the personnel with an improper grounding. This causes severe damage to the personnel as well as to the installations.
This is all about the electrical safety with detailed description. Hope that you might have get necessary and sufficient information regarding this topic. If you want more information related to this topic you can feel free to write us and also comment your suggestion on this.




2 Responses
The tips given on safety measures while working with electrical machines are very important. It should be followed properly to avoid accidents. Thanks for sharing.
Very useful article. I’m sure this will help all those who are planning to renovate and remodel their equipment with these safety precautions